Effect of Shenfu Injection on Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Pacemaker-Like Cells and Improvement of Pacing Function of Sinoatrial Node
- PMID: 35186186
- PMCID: PMC8853776
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4299892
Effect of Shenfu Injection on Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Pacemaker-Like Cells and Improvement of Pacing Function of Sinoatrial Node
Abstract
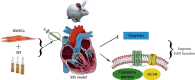
Sick sinus syndrome (SSS), a complex type of cardiac arrhythmia, is a major health threat to humans. Shenfu injection (SFI), a formula of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), is effective in improving bradyarrhythmia. However, the underlying mechanism of SFI's therapeutic effect is subject to few systematic investigations. The purpose of the present research is to examine whether SFI can boost the differentiation effectiveness of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) into pacemaker-like cells and whether the transplantation of these cells can improve the pacing function of the sinoatrial node (SAN) in a rabbit model of SSS. BMSCs from New Zealand rabbits were extracted, followed by incubation in vitro. The flow cytometry was utilized to identify the expression of CD29, CD44, CD90, and CD105 surface markers. The isolated BMSCs were treated with SFI, and the whole-cell patch-clamp method was performed to detect hyperpolarization-the activated cyclic nucleotide-gated potassium channel 4 (HCN4) channel current activation curve. The SSS rabbit model was established using the formaldehyde wet dressing method, and BMSCs treated with SFI were transplanted into the SAN of the SSS rabbit model. We detected changes in the body-surface electrocardiogram and recorded dynamic heart rate measurements. Furthermore, transplanted SFI-treated BMSCs were subjected to HE staining, TUNEL staining, qPCR, western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to study their characteristics. Our results indicate that the transplantation of SFI-treated BMSCs into the SAN of SSS rabbits improved the pacing function of the SAN. In vitro data showed that SFI induced the proliferation of BMSCs, promoted their differentiation capacity into pacemaker-like cells, and increased the HCN4 expression in BMSCs. In vivo, the transplantation of SFI treated-BMSCs preserved the function of SAN in SSS rabbits, improved the expression of the HCN4 gene and gap junction proteins (Cx43 and Cx45), and significantly upregulated the expression of cAMP in the SAN, compared to the SSS model group. In summary, the present research demonstrated that SFI might enhance the differentiation capacity of BMSCs into pacemaker-like cells, hence offering a novel approach for the development of biological pacemakers. Additionally, we confirmed the effectiveness and safety of pacemaker-like cells differentiated from BMSCs in improving the pacing function of the SAN.
Copyright © 2022 Qi Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors hereby declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Yixin-Fumai granules improve sick sinus syndrome in aging mice through Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway: A new target for sick sinus syndrome.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Sep 15;277:114254. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114254. Epub 2021 May 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34062246
-
Shenfu Injection: A Famous Chinese Prescription That Promotes HCN4 Activity in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 17;2021:9912844. doi: 10.1155/2021/9912844. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34457032 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of connexin 40 and hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel 4 in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cocultured with sinoatrial node tissues in vitro].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Feb;26(2):146-51. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22403875 Chinese.
-
Pacemaker activity of the human sinoatrial node: effects of HCN4 mutations on the hyperpolarization-activated current.Europace. 2014 Mar;16(3):384-95. doi: 10.1093/europace/eut348. Europace. 2014. PMID: 24569893 Review.
-
Rescuing cardiac automaticity in L-type Cav1.3 channelopathies and beyond.J Physiol. 2016 Oct 15;594(20):5869-5879. doi: 10.1113/JP270678. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27374078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Shenfu injection: a review of pharmacological effects on cardiovascular diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 14;15:1279584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1279584. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38420190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of Shenfu injection on bradyarrhythmia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 2;104(18):e41779. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041779. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40324250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mond H. G., Proclemer A. The 11th world survey of cardiac pacing and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: calendar year 2009--a World Society of Arrhythmia's project. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology . 2011;34(8):1013–1027. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

