Polydatin: A Critical Promising Natural Agent for Liver Protection via Antioxidative Stress
- PMID: 35186191
- PMCID: PMC8853764
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9218738
Polydatin: A Critical Promising Natural Agent for Liver Protection via Antioxidative Stress
Abstract
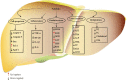
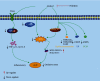
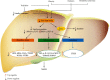
Polydatin, one of the natural active small molecules, was commonly applied in protecting and treating liver disorders in preclinical studies. Oxidative stress plays vital roles in liver injury caused by various factors, such as alcohol, viral infections, dietary components, drugs, and other chemical reagents. It is reported that oxidative stress might be one of the main reasons in the progressive development of alcohol liver diseases (ALDs), nonalcoholic liver diseases (NAFLDs), liver injury, fibrosis, hepatic failure (HF), and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this paper, we comprehensively summarized the pharmacological effects and potential molecular mechanisms of polydatin for protecting and treating liver disorders via regulation of oxidative stress. According to the previous studies, polydatin is a versatile natural compound and exerts significantly protective and curative effects on oxidative stress-associated liver diseases via various molecular mechanisms, including amelioration of liver function and insulin resistance, inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines, lipid accumulation, endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy, regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR, and activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), as well as increase of antioxidant enzymes (such as catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione reductase (GR), and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)). In addition, polydatin acts as a free radical scavenger against reactive oxygen species (ROS) by its phenolic and ethylenic bond structure. However, further clinical investigations are still needed to explore the comprehensive molecular mechanisms and confirm the clinical treatment effect of polydatin in liver diseases related to regulation of oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2022 Dandan Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective effects of polydatin from Polygonum cuspidatum against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46574. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046574. Epub 2012 Sep 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029551 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of polydatin against sulfur mustard-induced hepatic injury.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 15;367:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30677423
-
Polydatin alleviated alcoholic liver injury in zebrafish larvae through ameliorating lipid metabolism and oxidative stress.J Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Sep;138(1):46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2018.08.007. Epub 2018 Sep 7. J Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30245287
-
Polydatin for treating atherosclerotic diseases: A functional and mechanistic overview.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Aug;128:110308. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110308. Epub 2020 May 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32480216 Review.
-
The Neuroprotective Role of Polydatin: Neuropharmacological Mechanisms, Molecular Targets, Therapeutic Potentials, and Clinical Perspective.Molecules. 2021 Oct 2;26(19):5985. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195985. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of Kupffer cells in NAFLD and NASH: mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 16;11:1199519. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1199519. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37261074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oregano Essential Oil in Livestock and Veterinary Medicine.Animals (Basel). 2024 May 22;14(11):1532. doi: 10.3390/ani14111532. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polydatin retards the progression of osteoarthritis by maintaining bone metabolicbalance and inhibiting macrophage polarization.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Jan 7;12:1514483. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1514483. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39840130 Free PMC article.
-
Polydatin Prevents Electron Transport Chain Dysfunction and ROS Overproduction Paralleled by an Improvement in Lipid Peroxidation and Cardiolipin Levels in Iron-Overloaded Rat Liver Mitochondria.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 16;25(20):11104. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011104. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456885 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products for the treatment of chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment and prospects of nose-to-brain drug delivery.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 29;15:1292807. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1292807. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38348396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muriel P. Liver Pathophysiology . Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier; 2017. The Liver: General Aspects and Epidemiology.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

