LRP6 Polymorphisms Is Associated With Sudden Cardiac Death in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure in the Chinese Han Population
- PMID: 35187114
- PMCID: PMC8854291
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.815595
LRP6 Polymorphisms Is Associated With Sudden Cardiac Death in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure in the Chinese Han Population
Abstract
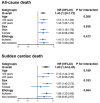
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) plays a critical role in cardiovascular homeostasis. The deficiency of LRP6 is associated with a high risk of arrhythmias. However, the association between genetic variations of LRP6 and sudden cardiac death (SCD) remains unknown. This study aims to explore the association between common variants of LRP6 and the prognosis of chronic heart failure (CHF) patients. From July 2005 to December 2009, patients with CHF were enrolled from 10 hospitals in China. The single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs2302684 was selected for the evaluation of the effect of LRP6 polymorphisms on the survival in patients with CHF. A total of 1,437 patients with CHF were finally included for the analysis. During a median follow-up of 61 months (range 0.4-129 months), a total of 546 (38.0%) patients died, including 201 (36.8%) cases with SCD and 345 (63.2%) cases with non-SCD. Patients carrying A allele of rs2302684 had an increased risk of all-cause death (adjusted HR 1.452, 95% CI 1.189-1.706; P < 0.001) and SCD (adjusted HR 1.783, 95% CI 1.337-2.378; P < 0.001). Therefore, the SNP rs2302684 T>A in LRP6 indicated higher risks of all-cause death and SCD in patients with CHF. LRP6 could be added as a novel predictor of SCD and might be a potential therapeutic target in the prevention of SCD in the CHF population.
Keywords: LRP6; chronic heart failure; prognosis; single-nucleotide polymorphism; sudden cardiac death.
Copyright © 2022 Guo, Lai, Chu, Chen, Gao, Sang, Dong, Pu and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Common Variants in TRDN and CALM1 Are Associated with Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death in Chronic Heart Failure Patients in Chinese Han Population.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 21;10(7):e0132459. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132459. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26196381 Free PMC article.
-
A common NOS1AP genetic polymorphism, rs12567209 G>A, is associated with sudden cardiac death in patients with chronic heart failure in the Chinese Han population.J Card Fail. 2014 Apr;20(4):244-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Jan 10. J Card Fail. 2014. PMID: 24418727
-
Common RyR2 variants associate with ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in chronic heart failure.Clin Sci (Lond). 2010 Jun 4;119(5):215-23. doi: 10.1042/CS20090656. Clin Sci (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20408814
-
Usefulness of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Predictors of Sudden Cardiac Death.Am J Cardiol. 2019 Jun 15;123(12):1900-1905. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.02.058. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Am J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31053292 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden cardiac death: a nationwide cohort study among the young.Dan Med J. 2016 Dec;63(12):B5321. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27910804 Review.
Cited by
-
Anomalous right coronary artery originating from the aorta: a series of nine pediatric cases.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Oct 31;23(1):546. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04377-4. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37907926 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy by regulating CTSD/HSP90α signaling during pressure overload.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Mar;46(3):606-617. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01415-4. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39779966
-
Clinical relevance of genetic polymorphisms in WNT signaling pathway (SFRP1, WNT3A, CTNNB1, WIF-1, DKK-1, LRP5, LRP6) on pulmonary tuberculosis in a Chinese population.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 7;13:1011700. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1011700. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36569862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, et al. . Heart disease and stroke statistics−2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. (2009) 119:e21–181. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.191261 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

