Penthorum Chinense Pursh Extract Alleviates Aflatoxin B1-Induced Liver Injury and Oxidative Stress Through Mitochondrial Pathways in Broilers
- PMID: 35187148
- PMCID: PMC8847786
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.822259
Penthorum Chinense Pursh Extract Alleviates Aflatoxin B1-Induced Liver Injury and Oxidative Stress Through Mitochondrial Pathways in Broilers
Abstract
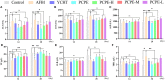
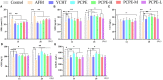
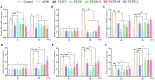
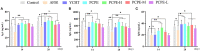
Aflatoxin is an important toxicant of the fungal origin and poses a threat to the poultry industry. This study was designed to reveal the underlying mechanism and protective methods against aflatoxin B1 (AFB1)-induced liver injury, oxidative stress, and apoptosis using a Traditional Chinese medicine, Penthorum chinense Pursh extract (PCPE), in broilers. A total of 164 (day-old) broilers were equally allocated to the control, AFB1 (3 mg/kg feed), positive drug (Yin-Chen-Hao Tang extract, 10 ml/kg feed), PCPE (2 g PCPE/kg), and PCPE low, medium, and high dose groups (1 g, 2 g, 3 g PCPE/kg feed, respectively). AFB1 significantly decreased the growth performance and serum immunoglobulin level, altered normal serum biochemical parameters and antioxidant activities, and induced histopathological lesions in the liver as compared to control group. Additionally, AFB1 significantly up-regulated the mRNA expression levels of apoptosis-related genes such as Bax, Bak, caspase-9, caspase-3, and p53, whereas it down-regulated the expression levels of BCL2 in the liver of broilers. The supplementation of different doses of PCPE to AFB1-affected birds significantly eased AFB1 negative effects by improving growth performance, immunoglobulin level, and oxidative capacity, and reversed oxidative stress and pathological lesions in liver. Furthermore, supplementation of PCPE to the AFB1 group reversed apoptosis by significantly down-regulating the mRNA expression levels of Bax, Bak, caspase-9, caspase-3, and p53 and up-regulating the expression levels of BCL2 in the liver of broilers. Based on these results, we conclude that supplementation of PCPE is protective and safe against oxidative stress, is anti-apoptotic, and reverses the liver damage caused by AFB1 in broilers.
Keywords: aflatoxin B1; apoptosis; broilers; liver; penthorum chinense pursh extract.
Copyright © 2022 Nabi, Tao, Ye, Li, Lu, Shang, Hu, Fang, Bhutto and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An Updated Review on Efficiency of Penthorum chinense Pursh in Traditional Uses, Toxicology, and Clinical Trials.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Feb 18;2023:4254051. doi: 10.1155/2023/4254051. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36852294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Penthorum chinense Prush extract alleviates aflatoxin B1-induced toxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis via mediating Nrf2 signaling pathway in the Bursa of Fabricius of broilers.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;275:109779. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2023.109779. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37871871
-
Penthorum chinense Pursh compound flavonoids supplementation alleviates Aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury via modulation of intestinal barrier and gut microbiota in broiler.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Apr 15;255:114805. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114805. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023. PMID: 36958264
-
Penthorum chinense Pursh Compound Ameliorates AFB1-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via Modulation of Mitochondrial Pathways in Broiler Chicken Kidneys.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Oct 8;8:750937. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.750937. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34692815 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of plant products and phytochemicals against aflatoxin toxicity in broiler chicken production: Present status.Toxicon. 2021 Sep;200:55-68. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2021.06.017. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Toxicon. 2021. PMID: 34228958 Review.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy of Additives for the Mitigation of Aflatoxins in Animal Feed: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 15;14(10):707. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100707. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287975 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine lactoferrin alleviates aflatoxin B1 induced hepatic and renal injury in broilers by mediating Nrf2 signaling pathway.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104316. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104316. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39383667 Free PMC article.
-
An Updated Review on Efficiency of Penthorum chinense Pursh in Traditional Uses, Toxicology, and Clinical Trials.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Feb 18;2023:4254051. doi: 10.1155/2023/4254051. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36852294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Supplementation of Novel Aflatoxin Oxidase CotA Alleviates Aflatoxin B1-Induced Oxidative Stress, Lipid Metabolism Disorder, and Apoptosis in the Liver of Japanese Quails.Animals (Basel). 2025 May 26;15(11):1555. doi: 10.3390/ani15111555. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40509021 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Penthorum Chinense Pursh Compound on AFB1-Induced Immune Imbalance via JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Spleen of Broiler Chicken.Vet Sci. 2023 Aug 13;10(8):521. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10080521. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37624308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali Rajput S, Sun L, Zhang N, Mohamed Khalil M, Gao X, Ling Z, et al. . Ameliorative effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on growth performance, immune function, antioxidant capacity, biochemical constituents, liver histopathology and aflatoxin residues in broilers exposed to aflatoxin B1. Toxins. (2017) 9:371. 10.3390/toxins9110371 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magnoli AP, Monge MP, Miazzo RD, Cavaglieri LR, Magnoli CE, Merkis CI, et al. . Effect of low levels of aflatoxin B1 on performance, biochemical parameters, and aflatoxin B1 in broiler liver tissues in the presence of monensin and sodium bentonite. Poult Sci. (2011) 90:48–58. 10.3382/ps.2010-00971 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

