Shenlian (SL) Decoction, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound, May Ameliorate Blood Glucose via Mediating the Gut Microbiota in db/db Mice
- PMID: 35187178
- PMCID: PMC8855168
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7802107
Shenlian (SL) Decoction, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound, May Ameliorate Blood Glucose via Mediating the Gut Microbiota in db/db Mice
Abstract
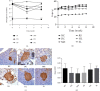
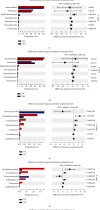
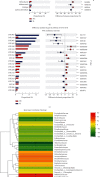
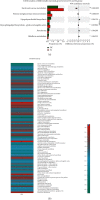
Shenlian (SL) decoction is a herbal formula composed of Coptis and ginseng, of which berberine and ginsenoside are the main constituents. Even though SL decoction is widely used in treating diabetes in China, the mechanism of its antidiabetes function still needs further study. Gut microbiota disorder is one of the important factors that cause diabetes. To explore the effect of SL decoction on intestinal microbiota, gut microbiota of mice was analyzed by sequencing the gut bacterial 16S rRNA V3+V4 region and metagenomics. In this study, results demonstrated that SL decoction had a better hypoglycemic effect and β cell protection effect than either ginseng or Coptis chinensis. Alpha diversity analysis showed that all interventions with ginseng, Coptis, and SL decoction could reverse the increased diversity and richness of gut microbiota in db/db mice. PCoA analysis showed oral SL decoction significantly alters gut microbiota composition in db/db mice. 395 OTUs showed significant differences after SL treatment, of which 37 OTUs enriched by SL decoction showed a significant negative correlation with FBG, and 204 OTUs decreased by SL decoction showed a significant positive correlation with FBG. Results of KEGG analysis and metagenomic sequencing showed that SL decoction could reduce the Prevotellaceae, Rikenellaceae, and Helicobacteraceae, which were related to lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis, riboflavin metabolism, and peroxisome, respectively. It could also upregulate the abundance of Bacteroidaceae, which contributed to the metabolism of starch and sucrose as well as pentose-glucuronate interconversions. In the species level, SL decoction significantly upregulates the relative abundance of Bacteroides_acidifaciens which showed a significant negative correlation with FBG and was reported to be a potential agent for modulating metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity. In conclusion, SL decoction was effective in hypoglycemia and its mechanism may be related to regulating gut microbiota via upregulating Bacteroides_acidifaciens.
Copyright © 2022 Rui-xi Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
16S rRNA Sequencing and Metagenomics Study of Gut Microbiota: Implications of BDB on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Mar Drugs. 2020 Sep 17;18(9):469. doi: 10.3390/md18090469. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32957565 Free PMC article.
-
Oil tea improves glucose and lipid levels and alters gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice.Nutr Res. 2018 Sep;57:67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Nutr Res. 2018. PMID: 30122197
-
Effect of RG (Coptis root and ginseng) formula in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a study protocol for a randomized controlled and double-blinding trial.Trials. 2022 Apr 14;23(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06229-5. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35422046 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of traditional Chinese medicine on gut microbiota in adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jul 15;88:153455. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153455. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33478831
-
Could the gut microbiota reconcile the oral bioavailability conundrum of traditional herbs?J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:253-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.031. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26723469 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut Microbiota-Targeted Intervention of Hyperlipidemia Using Monascus-Fermented Ginseng.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 30;18(5):661. doi: 10.3390/ph18050661. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430481 Free PMC article.
-
Shenlian Decoction Ameliorates LPS-Related Inflammation in db/db Mice: Coupling Network Pharmacology With Experimental Verification.J Diabetes Res. 2025 Jan 6;2025:3823051. doi: 10.1155/jdr/3823051. eCollection 2025. J Diabetes Res. 2025. PMID: 39810933 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapeutics for Metabolic Disorders: Mechanistic Insights into the Synergy of Probiotic-Fermented Herbal Bioactives.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 7;26(12):5486. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125486. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of traditional Chinese medicine affecting gut microbiota in obesity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 1;14:1149751. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1149751. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36936157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Managing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via the Regulation of Gut Microbiota: A Chinese Medicine Perspective.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 18;16(22):3935. doi: 10.3390/nu16223935. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39599721 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice . 2019;157:p. 107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

