Thymocytes trigger self-antigen-controlling pathways in immature medullary thymic epithelial stages
- PMID: 35188458
- PMCID: PMC8860447
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.69982
Thymocytes trigger self-antigen-controlling pathways in immature medullary thymic epithelial stages
Abstract
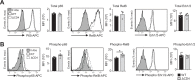
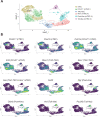
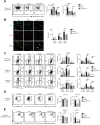
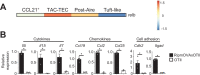
Interactions of developing T cells with Aire+ medullary thymic epithelial cells expressing high levels of MHCII molecules (mTEChi) are critical for the induction of central tolerance in the thymus. In turn, thymocytes regulate the cellularity of Aire+ mTEChi. However, it remains unknown whether thymocytes control the precursors of Aire+ mTEChi that are contained in mTEClo cells or other mTEClo subsets that have recently been delineated by single-cell transcriptomic analyses. Here, using three distinct transgenic mouse models, in which antigen presentation between mTECs and CD4+ thymocytes is perturbed, we show by high-throughput RNA-seq that self-reactive CD4+ thymocytes induce key transcriptional regulators in mTEClo and control the composition of mTEClo subsets, including Aire+ mTEChi precursors, post-Aire and tuft-like mTECs. Furthermore, these interactions upregulate the expression of tissue-restricted self-antigens, cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules important for T-cell development. This gene activation program induced in mTEClo is combined with a global increase of the active H3K4me3 histone mark. Finally, we demonstrate that these self-reactive interactions between CD4+ thymocytes and mTECs critically prevent multiorgan autoimmunity. Our genome-wide study thus reveals that self-reactive CD4+ thymocytes control multiple unsuspected facets from immature stages of mTECs, which determines their heterogeneity.
Keywords: T cells; cellular crosstalk; immunology; inflammation; medullary thymic epithelial cells; mouse; thymus; tolerance.
© 2022, Lopes et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NL, NB, JS, NP, JC, PF, MG, MI No competing interests declared
Figures

















References
-
- Akiyama T, Shimo Y, Yanai H, Qin J, Ohshima D, Maruyama Y, Asaumi Y, Kitazawa J, Takayanagi H, Penninger JM, Matsumoto M, Nitta T, Takahama Y, Inoue J-I. The tumor necrosis factor family receptors RANK and CD40 cooperatively establish the thymic medullary microenvironment and self-tolerance. Immunity. 2008;29:423–437. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.06.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akiyama N, Shinzawa M, Miyauchi M, Yanai H, Tateishi R, Shimo Y, Ohshima D, Matsuo K, Sasaki I, Hoshino K, Wu G, Yagi S, Inoue J, Kaisho T, Akiyama T. Limitation of immune tolerance-inducing thymic epithelial cell development by Spi-B-mediated negative feedback regulation. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2014;211:2425–2438. doi: 10.1084/jem.20141207. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

