Defective perlecan-associated basement membrane regeneration and altered modulation of transforming growth factor beta in corneal fibrosis
- PMID: 35188596
- PMCID: PMC8972081
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-022-04184-7
Defective perlecan-associated basement membrane regeneration and altered modulation of transforming growth factor beta in corneal fibrosis
Abstract
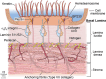
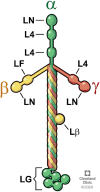
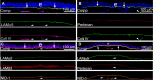
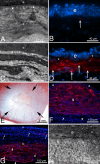
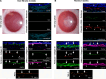
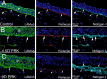
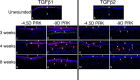
In the cornea, the epithelial basement membrane (EBM) and corneal endothelial Descemet's basement membrane (DBM) critically regulate the localization, availability and, therefore, the functions of transforming growth factor (TGF)β1, TGFβ2, and platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF) that modulate myofibroblast development. Defective regeneration of the EBM, and notably diminished perlecan incorporation, occurs via several mechanisms and results in excessive and prolonged penetration of pro-fibrotic growth factors into the stroma. These growth factors drive mature myofibroblast development from both corneal fibroblasts and bone marrow-derived fibrocytes, and then the persistence of these myofibroblasts and the disordered collagens and other matrix materials they produce to generate stromal scarring fibrosis. Corneal stromal fibrosis often resolves completely if the inciting factor is removed and the BM regenerates. Similar defects in BM regeneration are likely associated with the development of fibrosis in other organs where perlecan has a critical role in the modulation of signaling by TGFβ1 and TGFβ2. Other BM components, such as collagen type IV and collagen type XIII, are also critical regulators of TGF beta (and other growth factors) in the cornea and other organs. After injury, BM components are dynamically secreted and assembled through the cooperation of neighboring cells-for example, the epithelial cells and keratocytes for the corneal EBM and corneal endothelial cells and keratocytes for the corneal DBM. One of the most critical functions of these reassembled BMs in all organs is to modulate the pro-fibrotic effects of TGFβs, PDGFs and other growth factors between tissues that comprise the organ.
Keywords: Basement membrane assembly; Collagen type IV; Cornea; Descemet’s membrane; Dystroglycan; Epithelial barrier function; Epithelial basement membrane; HGF; Integrins; KGF; Laminins; Nidogens; PDGF; Perlecan; Regeneration; TGF beta.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The author does not have any commercial or proprietary interests in the subject matter of this review article.
Figures
References
-
- Yurchenco PD, O’Rear J. Supramolecular organization of basement membranes. In: Rohrbach DH, Timpl R, editors. Molecular and cellular aspects of basement membranes. San Diego: Academic Press; 1993. pp. 20–47.
-
- Martinez-Hernandez A, Amenta PS. The basement membrane in pathology. Lab Invest. 1983;48:656–677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

