An estimate of the deepest branches of the tree of life from ancient vertically evolving genes
- PMID: 35190025
- PMCID: PMC8890751
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.66695
An estimate of the deepest branches of the tree of life from ancient vertically evolving genes
Abstract
Core gene phylogenies provide a window into early evolution, but different gene sets and analytical methods have yielded substantially different views of the tree of life. Trees inferred from a small set of universal core genes have typically supported a long branch separating the archaeal and bacterial domains. By contrast, recent analyses of a broader set of non-ribosomal genes have suggested that Archaea may be less divergent from Bacteria, and that estimates of inter-domain distance are inflated due to accelerated evolution of ribosomal proteins along the inter-domain branch. Resolving this debate is key to determining the diversity of the archaeal and bacterial domains, the shape of the tree of life, and our understanding of the early course of cellular evolution. Here, we investigate the evolutionary history of the marker genes key to the debate. We show that estimates of a reduced Archaea-Bacteria (AB) branch length result from inter-domain gene transfers and hidden paralogy in the expanded marker gene set. By contrast, analysis of a broad range of manually curated marker gene datasets from an evenly sampled set of 700 Archaea and Bacteria reveals that current methods likely underestimate the AB branch length due to substitutional saturation and poor model fit; that the best-performing phylogenetic markers tend to support longer inter-domain branch lengths; and that the AB branch lengths of ribosomal and non-ribosomal marker genes are statistically indistinguishable. Furthermore, our phylogeny inferred from the 27 highest-ranked marker genes recovers a clade of DPANN at the base of the Archaea and places the bacterial Candidate Phyla Radiation (CPR) within Bacteria as the sister group to the Chloroflexota.
Keywords: evolutionary biology; microbial diversity; molecular evolution; none; phylogenetics; tree of life.
© 2022, Moody et al.
Conflict of interest statement
EM, TM, ND, JC, CP, PO, GS, AS, TW No competing interests declared
Figures


















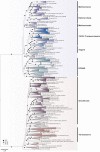



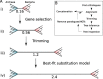
Similar articles
-
The effects of model choice and mitigating bias on the ribosomal tree of life.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013 Oct;69(1):17-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 May 22. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013. PMID: 23707703
-
Bacterial Origin and Reductive Evolution of the CPR Group.Genome Biol Evol. 2020 Mar 1;12(3):103-121. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa024. Genome Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 32031619 Free PMC article.
-
Early evolutionary relationships among known life forms inferred from elongation factor EF-2/EF-G sequences: phylogenetic coherence and structure of the archaeal domain.J Mol Evol. 1992 May;34(5):396-405. doi: 10.1007/BF00162996. J Mol Evol. 1992. PMID: 1602493
-
Major New Microbial Groups Expand Diversity and Alter our Understanding of the Tree of Life.Cell. 2018 Mar 8;172(6):1181-1197. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.016. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29522741 Review.
-
Protein based molecular markers provide reliable means to understand prokaryotic phylogeny and support Darwinian mode of evolution.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Jul 26;2:98. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00098. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22919687 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The nature of the last universal common ancestor and its impact on the early Earth system.Nat Ecol Evol. 2024 Sep;8(9):1654-1666. doi: 10.1038/s41559-024-02461-1. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Nat Ecol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38997462 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific novelty beyond the experiment.Microb Biotechnol. 2023 Jun;16(6):1131-1173. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14222. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Microb Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36786388 Free PMC article.
-
The Last Universal Common Ancestor of Ribosome-Encoding Organisms: Portrait of LUCA.J Mol Evol. 2024 Oct;92(5):550-583. doi: 10.1007/s00239-024-10186-9. Epub 2024 Aug 19. J Mol Evol. 2024. PMID: 39158619 Review.
-
GTPase Era at the heart of ribosome assembly.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Oct 4;10:1263433. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1263433. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37860580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the Origin and Evolution of Microbial Mercury Methylation.Genome Biol Evol. 2023 Apr 6;15(4):evad051. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evad051. Genome Biol Evol. 2023. PMID: 36951100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aghanim N. Planck 2018 Results. VI. Cosmological Parameters. arXiv. 2018 https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.06209
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

