Surgical outcomes after neoadjuvant nivolumab or nivolumab with ipilimumab in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35190177
- PMCID: PMC10228712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2022.01.019
Surgical outcomes after neoadjuvant nivolumab or nivolumab with ipilimumab in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Surgical outcomes for non-small cell lung cancer after neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitors continue to be debated. We assessed perioperative outcomes of patients treated with Nivolumab or Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab (NEOSTAR) and compared them with patients treated with chemotherapy or previously untreated patients with stage I-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer.
Methods: Forty-four patients with stage I to IIIA non-small cell lung cancer (American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Manual, seventh edition) were randomized to nivolumab (N; 3 mg/kg intravenously on days 1, 15, and 29; n = 23) or nivolumab with ipilimumab (NI; I, 1 mg/kg intravenously on day 1; n = 21). Curative-intent operations were planned between 3 and 6 weeks after the last dose of neoadjuvant N. Patients who completed resection upfront or after chemotherapy from the same time period were used as comparison.
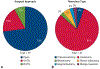
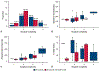
Results: In the N arm, 21 (91%) were resected on-trial, 1 underwent surgery off-trial, and one was not resected (toxicity-related). In the NI arm, 16 (76%) resections were performed on-trial, one off-trial, and 4 were not resected (none toxicity-related). Median time to operation was 31 days, and consisted of 2 (5%) pneumonectomies, 33 (89%) lobectomies, and 1 (3%) each of segmentectomy and wedge resection. The approach was 27 (73%) thoracotomy, 7 (19%) thoracoscopy, and 3 (8%) robotic-assisted. Conversion occurred in 17% (n = 2/12) of minimally invasive cases. All 37 achieved R0 resection. Pulmonary, cardiac, enteric, neurologic, and wound complications occurred in 9 (24%), 4 (11%), 2 (5%), 1 (3%), and 1 (3%) patient, respectively. The 30- and 90-day mortality rate was 0% and 2.7% (n = 1), respectively. Postoperative complication rates were comparable with lung resection upfront or after chemotherapy.
Conclusions: Operating after neoadjuvant N or NI is overall safe and effective and yields perioperative outcomes similar to those achieved after chemotherapy or upfront resection.
Keywords: immunotherapy; ipilimumab; lobectomy; lung resection; lung surgery; neoadjuvant; nivolumab.
Copyright © 2022 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Commentary: To whom much is given much will be required.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Nov;164(5):1338-1339. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2022.02.018. Epub 2022 Feb 12. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 35279292 No abstract available.
References
-
- Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. Springer International Publishing; 2017.
-
- Pignon JP, Tribodet H, Scagliotti GV, Douillard JY, Shepard FA, Stephens RJ, et al. Lung adjuvant cisplatin evaluation: a pooled analysis by the LACE Collaborative Group. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3552–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

