Ulcerative colitis is characterized by a plasmablast-skewed humoral response associated with disease activity
- PMID: 35190725
- PMCID: PMC9107072
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01680-y
Ulcerative colitis is characterized by a plasmablast-skewed humoral response associated with disease activity
Abstract
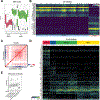
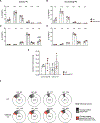
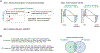
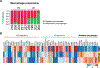
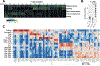
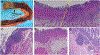
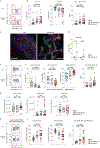
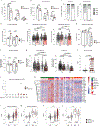
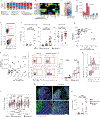
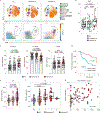
B cells, which are critical for intestinal homeostasis, remain understudied in ulcerative colitis (UC). In this study, we recruited three cohorts of patients with UC (primary cohort, n = 145; validation cohort 1, n = 664; and validation cohort 2, n = 143) to comprehensively define the landscape of B cells during UC-associated intestinal inflammation. Using single-cell RNA sequencing, single-cell IgH gene sequencing and protein-level validation, we mapped the compositional, transcriptional and clonotypic landscape of mucosal and circulating B cells. We found major perturbations within the mucosal B cell compartment, including an expansion of naive B cells and IgG+ plasma cells with curtailed diversity and maturation. Furthermore, we isolated an auto-reactive plasma cell clone targeting integrin αvβ6 from inflamed UC intestines. We also identified a subset of intestinal CXCL13-expressing TFH-like T peripheral helper cells that were associated with the pathogenic B cell response. Finally, across all three cohorts, we confirmed that changes in intestinal humoral immunity are reflected in circulation by the expansion of gut-homing plasmablasts that correlates with disease activity and predicts disease complications. Our data demonstrate a highly dysregulated B cell response in UC and highlight a potential role of B cells in disease pathogenesis.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Macpherson AJ & Uhr T Induction of protective IgA by intestinal dendritic cells carrying commensal bacteria. Science 303, 1662–1665 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Peterson DA, McNulty NP, Guruge JL & Gordon JI IgA response to symbiotic bacteria as a mediator of gut homeostasis. Cell Host Microbe 2, 328–339 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Bollinger RR et al. Secretory IgA and mucin-mediated biofilm formation by environmental strains of Escherichia coli: role of type 1 pili. Mol. Immunol 43, 378–387 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Geissmann F et al. A subset of human dendritic cells expresses IgA Fc receptor (CD89), which mediates internalization and activation upon cross-linking by IgA complexes. J. Immunol 166, 346–352 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

