Overview of tau PET molecular imaging
- PMID: 35191407
- PMCID: PMC9011369
- DOI: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000001035
Overview of tau PET molecular imaging
Abstract
Purpose of review: This article reviews tau PET imaging with an emphasis on first-generation and second-generation tau radiotracers and their application in neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease and non-Alzheimer's disease tauopathies.
Recent findings: Tau is a critical protein, abundant in neurons within the central nervous system, which plays an important role in maintaining microtubules by binding to tubulin in axons. In its abnormal hyperphosphorylated form, accumulation of tau has been linked to a variety of neurodegenerative disorders, collectively referred to as tauopathies, which include Alzheimer's disease and non-Alzheimer's disease tauopathies [e.g., corticobasal degeneration (CBD), argyrophilic grain disease, progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), and Pick's disease]. A number of first-generation and second-generation tau PET radiotracers have been developed, including the first FDA-approved agent [18F]-flortaucipir, which allow for in-vivo molecular imaging of underlying histopathology antemortem, ultimately guiding disease staging and development of disease-modifying therapeutics.
Summary: Tau PET is an emerging imaging modality in the diagnosis and staging of tauopathies.
Copyright © 2022 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
Dr Gordon has received research support without direct compensation from Eisai, AbbVie, Janssen, and Novo Nordisk, and has been a consultant for METiS Pharmaceuticals. Dr Franceschi has received research support without direct compensation from Life Molecular Imaging GmbH, and has served as a consultant for Biogen Inc and Life Molecular Imaging GmbH. Dr Chiang has served as a consultant for Biogen Inc. and Life Molecular Imaging GmbH.
Figures
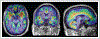
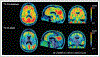
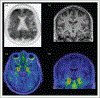
References
-
- Food and Drug Administration. URL: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-d.... [Accessed date 1st Oct 2021]
-
- Neve RL, Harris P, Kosik KS, et al. Identification of cDNA clones for the human microtubule-associated protein tau and chromosomal localization of the genes for tau and microtubule-associated protein 2. Brain Res 1986; 387:271–280. - PubMed
-
-
Shi Y, Zhang W, Yang Y, et al. Structure-based classification of tauopathies. Nature 2021; 598:359–363.
Study outlines a hierarchical classification of tauopathies on the basis of their filament folds, which complements clinical diagnosis and neuropathology and also allows the identification of new entities.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

