Straightforward Synthesis of α-Chloromethylketimines Catalyzed by Gold(I). A Clean Way to Building Blocks
- PMID: 35191705
- PMCID: PMC10391627
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c02877
Straightforward Synthesis of α-Chloromethylketimines Catalyzed by Gold(I). A Clean Way to Building Blocks
Abstract
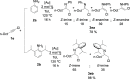
α-Chloromethylketimines have been obtained through a gold-catalyzed hydroamination of aromatic and aliphatic 1-chloroalkynes with aromatic amines by using equimolar amounts of both reagents. This procedure has allowed the preparation and spectroscopic characterization of α-chloromethylketimines for the first time with a high degree of purity, complete conversion, and atom economy. The synthetic usefulness of the methodology has been demonstrated with the preparation of β-chloroamines and indoles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- De Kimpe N.; Verhé R. In The Chemistry of α-Haloketones, α-Haloaldehydes and α-Haloimines; Wiley-VCH: Chichester, U.K., 1988; Chapter 2 and Appendix, pp 225–368.
-
- De Kimpe N.; Stevens C. A Convenient Method for the Synthesis of β-chloroamines by Electrophilic Reduction of α-Chloroimines. Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 3407–3416. 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)86404-8. - DOI
- Malkov A. V.; Vranková K.; Stončius S.; Kočovský P. Asymmetric Reduction of Imines with Trichlorosilane Catalyzed by Sigamide, an Amino Acid-Derived Formamide: Scope and Limitations. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 5839–5849. 10.1021/jo900561h. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sweeney J. B. Aziridines: epoxides’ ugly cousins?. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2002, 31, 247–258. 10.1039/B006015L. - DOI - PubMed
- Mack D. J.; Njardarson J. T. Recent Advances in the Metal-Catalyzed Ring Expansions of Three- and Four-Membered Rings. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 272–286. 10.1021/cs300771d. - DOI
- Huang C. Y.; Doyle A. G. The Chemistry of Transition Metals with Three-Membered Ring Heterocycles. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8153–8198. 10.1021/cr500036t. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bellezza D.; Noverges B.; Fasano F.; Sarmiento J. T.; Medio-Simón M.; Asensio G. Palladium-Catalyzed C–C Ring Closure in α-Chloromethylimines: Synthesis of 1H-Indoles. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1229–1235. 10.1002/ejoc.201801607. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources