Evaluation of the post-processing algorithms SimGrid and S-Enhance for paediatric intensive care patients and neonates
- PMID: 35192022
- PMCID: PMC9107410
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-021-05279-2
Evaluation of the post-processing algorithms SimGrid and S-Enhance for paediatric intensive care patients and neonates
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Evaluation of the post‑processing algorithms SimGrid and S‑Enhance for paediatric intensive care patients and neonates.Pediatr Radiol. 2022 May;52(6):1197. doi: 10.1007/s00247-022-05353-3. Pediatr Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35376980 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
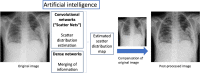
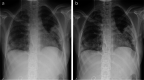
Background: Post-processing software can be used in digital radiography to achieve higher image quality, especially in cases of scattered radiation. SimGrid is a grid-like software based on a Convolutional Neuronal Network that estimates the distribution and degree of scattered radiation in radiographs and thus improves image quality by simulating an anti-scatter grid. S-Enhance is an algorithm programmed to improve contrast visibility of foreign material.
Objective: The objective of this study was to evaluate the SimGrid and S-Enhance digital radiography post-processing methods for neonatology and paediatric intensive care.
Materials and methods: Two hundred and ten radiographs from the neonatal (n = 101, 0 to 6 months of age) and paediatric (n = 109, 6 months to 18 years of age) intensive care units performed in daily clinical routine using a mobile digital radiography system were post-processed with one of the algorithms, anonymized and then evaluated comparatively by two experienced paediatric radiologists. For every radiograph, patient data and exposure data were collected and analysed.
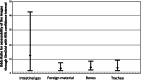
Results: Analysis of different radiographs showed that SimGrid significantly improves image quality for patients with a weight above 10 kg (range: 10-30 kg: odds ratio [OR] = 6.683, P < 0.0001), especially regarding the tracheobronchial system, intestinal gas, and bones. Utilizing S-Enhance significantly advances the assessment of foreign material (OR = 136.111, P < 0.0001) and bones (OR = 34.917, P < 0.0001) for children of all ages and weight, whereas overall image quality decreases.
Conclusion: SimGrid offers a differentiated spectrum in image improvement for children beyond the neonatal period whereas S-Enhance especially improves visibility of foreign material and bones for all patients.
Keywords: Deep learning; Digital radiography; Image enhancement; Neonatal intensive care unit; Pediatric intensive care unit; Radiation dosage; Radiography.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures






References
-
- McWilliam R, Scott P, Crone B, Ratcliffe A (2020) Composition-guided post processing-a new level of image quality in digital radiography. European Congress of Radiology
-
- Hsieh SA, CA, US) (2016) X-RAY ANTI-SCATTER GRID WITH VARYING GRID RATIO. Hsieh Scott, United States https://www.freepatentsonline.com/y2016/0328836.html
-
- Lee B, Song J, Kim D, Oh H (2017) Improving the Image Quality with a Novel Software-based Scatter Correction: SimGrid™ Technology, Medical Imaging R&D, Health & Medical Equipment Business, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. WP201709-DR-SimGridTM
-
- Lee S (2018) Radiation dose reduction in digital radiography – no compromise in image quality. Clinical Research group, Health & Medical Equipment Business, Samsung Electronics Co., https://www.dieurope.com/pdf/138407.pdf. Accessed 28 Dec 2020
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

