Genetic regulation of the ompX porin of Salmonella Typhimurium in response to hydrogen peroxide stress
- PMID: 35193678
- PMCID: PMC8862304
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-022-00377-3
Genetic regulation of the ompX porin of Salmonella Typhimurium in response to hydrogen peroxide stress
Abstract
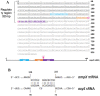
Background: Salmonella Typhimurium is a Gram-negative pathogen that causes a systemic disease in mice resembling typhoid fever. During its infective cycle, S. Typhimurium is phagocytized by macrophages and proliferates inside a Salmonella-containing vacuole where Salmonella is exposed and survives oxidative stress induced by H2O2 through modulation of gene expression. After exposure of Salmonella to H2O2, the expression of the porin-encoding gene ompX increases, as previously shown by microarray analysis. Expression of ompX mRNA is regulated at a post-transcriptional level by MicA and CyaR sRNAs in aerobiosis. In addition, sequence analysis predicts a site for OxyS sRNA in ompX mRNA.
Results: In this work we sought to evaluate the transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of ompX under H2O2 stress. We demonstrate that ompX expression is induced at the transcriptional level in S. Typhimurium under such conditions. Unexpectedly, an increase in ompX gene transcript and promoter activity after challenges with H2O2 does not translate into increased protein levels in the wild-type strain, suggesting that ompX mRNA is also regulated at a post-transcriptional level, at least under oxidative stress. In silico gene sequence analysis predicted that sRNAs CyaR, MicA, and OxyS could regulate ompX mRNA levels. Using rifampicin to inhibit mRNA expression, we show that the sRNAs (MicA, CyaR and OxyS) and the sRNA:mRNA chaperone Hfq positively modulate ompX mRNA levels under H2O2-induced stress in Salmonella during the exponential growth phase in Lennox broth.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that ompX mRNA is regulated in response to H2O2 by the sRNAs CyaR, MicA and OxyS is Salmonella Typhimurium.
Keywords: H2O2 stress; Transcriptional regulation; Translational regulation; ompX.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Cabezas CE, Briones AC, Aguirre C, Pardo-Esté C, Castro-Severyn J, Salinas CR, Baquedano MS, Hidalgo AA, Fuentes J, A., Morales, E. H., Meneses, C. A., Castro-Nallar, E., & Saavedra, C. P. The transcription factor SlyA from Salmonella Typhimurium regulates genes in response to hydrogen peroxide and sodium hypochlorite. Res Microbiol. 2018;169(6):263–278. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2018.04.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

