The Mediator kinase module: an interface between cell signaling and transcription
- PMID: 35193797
- PMCID: PMC8939868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.01.002
The Mediator kinase module: an interface between cell signaling and transcription
Abstract
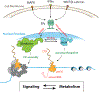
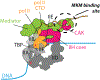
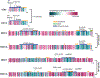
The Mediator complex controls RNA polymerase II (pol II) activity by coordinating the assembly of pol II regulatory factors at transcription start sites and by mediating interactions between enhancer-bound transcription factors (TFs) and the pol II enzyme. Mediator structure and function is completely altered upon binding the Mediator kinase module, a multi-subunit complex that contains CDK8 or its vertebrate-specific paralog CDK19. Here, we review the mechanisms by which the Mediator kinase module controls pol II transcription, emphasizing its impact on TF activity, pol II elongation, enhancer function, and chromatin architecture. We also highlight how the Mediator kinase module integrates signaling pathways with transcription to enable rapid, stimulus-specific responses, as well as its links to human disease.
Keywords: MED12; MED13; eRNA; enhancer-promoter loops; metabolism; pol II pausing.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.J.T. is a member of the SAB at Dewpoint Therapeutics.
Figures
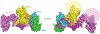

References
-
- Rocha PP et al. (2010) Med12 is essential for early mouse development and for canonical Wnt and Wnt/PCP signaling. Development 137 (16), 2723–31. - PubMed
-
- Schneider EV et al. (2011) The structure of CDK8/CycC implicates specificity in the CDK/cyclin family and reveals interaction with a deep pocket binder. J Mol Biol 412 (2), 251–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

