ISA101 and nivolumab for HPV-16+ cancer: updated clinical efficacy and immune correlates of response
- PMID: 35193933
- PMCID: PMC9066369
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004232
ISA101 and nivolumab for HPV-16+ cancer: updated clinical efficacy and immune correlates of response
Abstract
Background: The combination of ISA101, a human papilloma virus (HPV) 16 peptide vaccine, and nivolumab showed a promising response rate of 33% in patients with incurable HPV-16+ cancer. Here we report long-term clinical outcomes and immune correlates of response.
Methods: Patients with advanced HPV-16+ cancer and less than two prior regimens for recurrence were enrolled to receive ISA101 (100 µg/peptide) on days 1, 22, and 50 and nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks beginning day 8 for up to 1 year. Baseline tumor samples were stained with multiplex immunofluorescence for programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1), CD3, CD8, CD68, and pan-cytokeratin in a single panel and scanned with the Vectra 3.0 multispectral microscope. Whole transcriptome analysis of baseline tumors was performed with Affymetrix Clariom D arrays. Differential gene expression analysis was performed on responders versus non-responders.
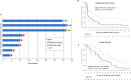
Results: Twenty-four patients were followed for a median of 46.5 months (95% CI, 46.0 months to not reached (NR)). The median duration of response was 11.2 months (95% CI, 8.51 months to NR); three out of eight (38%) patients with objective response were without progression at 3 years. The median and 3-year overall survival were 15.3 months (95% CI, 10.6 months to 27.2 months) and 12.5% (95% CI, 4.3% to 36%), respectively. The scores for activated T cells ((CD3+PD-1+)+(CD3+CD8+PD-1+)), activated cytotoxic T cells (CD3+CD8+PD-1+), and total macrophage ((CD68+PD-L1-)+(CD68+PD-L1+)) in tumor were directly correlated with clinical response (p<0.05) and depth of response with the two complete response patients having the highest degree of CD8+ T cells. Gene expression analysis revealed differential regulation of 357 genes (≥1.25 fold) in non-responders versus responders (p<0.05). Higher expression of immune response, inflammatory response and interferon-signaling pathway genes were correlated with clinical response (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Efficacy of ISA101 and nivolumab remains promising in long-term follow-up. Increased infiltration by PD-1+ T cells and macrophages was predictive of response. Enrichment in gene sets associated with interferon-γ response and immune infiltration strongly predicted response to therapy. A randomized trial is ongoing to test this strategy and to further explore correlates of immune response with combined nivolumab and ISA101, versus nivolumab alone.
Trial registration number: NCT02426892.
Keywords: head and neck neoplasms; immunogenicity; immunotherapy; tumor microenvironment; vaccine.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RF: reports personal fees from Regeneron-Sanofi, Ayala Pharmaceuticals, Klus Pharma, Bicara Therapeutics, Medscape, Carevive systems, G1 Therapeutics, Prelude Therapeutics, Merck, and Intellisphere in the past 36 months outside of the submitted work; and institutional fees from AstraZeneca, Merck, Genentech, Pfizer, Rakuten, Nanobiotix, and EMD Serono in the past 36 months. WW has received honoraria/speaker’s fees and/or participated in advisory boards from Roche/Genentech, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Merck, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Takeda, Janssen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sanofi Aventis. CJMM is Chief Scientific Officer of ISA Pharmaceuticals, a biotech company aiming at registration of a long peptide vaccine very similar to the one studied in this manuscript. MAC reports grants and personal fees from ImmunoGenesis, Inc. and ImmunoMet, Inc., personal fees from Alligator Bioscience, Inc., ImmunOS, Inc., Oncoresponse, Inc., Pieris, Inc., Nurix, Inc., Aptevo, Inc., Servier, Inc., Kineta, Inc., Salarius, Inc., Xencor, Inc., Agenus, Inc., Mereo, Inc., Astrazeneca, Inc., Amunix, Inc., Adagene, Inc., outside the submitted work; In addition, Dr. Curran has a patent Methods and Composition for Localized Secretion of Anti-CTLA-4 Antibodies with royalties paid by multiple licensees, a patent Dual specificity antibodies which bind both PD-L1 and PD-L2 and prevent their binding to PD-1 with royalties paid by ImmunoGenesis, Inc. IIW reports consults fees from ROCHE, Bayer, BMS, Astra Zeneca, Pfizer, HTG molecular, Merck, ClaxoSmithKline, Guardant Health, Novartis, Flame, Sanofi, Janssen, Daiichi Sankyo, Oncocyte, Amgen, MSD, Medcape; honoraria from Medscape, Roche, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Platform Health, Merck; and Grants from Genetech, HTG Molecular, Merck, BMS, Medimmune, Adaptive, Adaptimmune, EMD Serono, Pfizer, Takeda, Amgen, Karus, Johnson & Johnson, Bayer, Iovance, 4D, Novartis, Akova. JJL reports he received grant from Cancer Center Support Grant (CCSG) P30 CA016672 from National Cancer Institute. BG reports consult fees from Regeneron and grants from Pfizer Inc, ISA Pharmaceuticals, and Medimmune.
Figures


References
-
- Cohen EEW, Soulières D, Le Tourneau C, et al. . Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. The Lancet 2019;393:156–67. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31999-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
