COVID-19 Pandemic: Identifying Key Issues Using Social Media and Natural Language Processing
- PMID: 35194569
- PMCID: PMC8853170
- DOI: 10.1007/s41666-021-00111-w
COVID-19 Pandemic: Identifying Key Issues Using Social Media and Natural Language Processing
Abstract
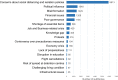
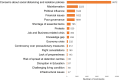
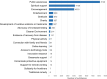
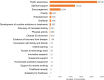
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected people's lives in many ways. Social media data can reveal public perceptions and experience with respect to the pandemic, and also reveal factors that hamper or support efforts to curb global spread of the disease. In this paper, we analyzed COVID-19-related comments collected from six social media platforms using natural language processing (NLP) techniques. We identified relevant opinionated keyphrases and their respective sentiment polarity (negative or positive) from over 1 million randomly selected comments, and then categorized them into broader themes using thematic analysis. Our results uncover 34 negative themes out of which 17 are economic, socio-political, educational, and political issues. Twenty (20) positive themes were also identified. We discuss the negative issues and suggest interventions to tackle them based on the positive themes and research evidence.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Health informatics; Keyphrase extraction; Natural language processing; Social media; Text mining; Thematic analysis.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Jilani TN, Jamil RT, Siddiqui AH (2021) H1N1 Influenza. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL)
-
- Dawood FS, Iuliano AD, Reed C, Meltzer MI, Shay DK, Cheng PY, Bandaranayake D, Breiman RF, Brooks WA, Buchy P, Feikin DR, Fowler KB, Gordon A, Hien NT, Horby P, Huang QS, Katz MA, Krishnan A, Lal R, Montgomery JM, Mølbak K, Pebody R, Presanis AM, Razuri H, Steens A, Tinoco YO, Wallinga J, Yu H, Vong S, Bresee J, Widdowson MA. Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: a modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:687–695. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70121-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (2019) HIV/AIDS. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids. Accessed 16 May 2020
-
- Tian H, Liu Y, Li Y, Wu C-H, Chen B, Kraemer MUG, Li B, Cai J, Xu B, Yang Q, Wang B, Yang P, Cui Y, Song Y, Zheng P, Wang Q, Bjornstad ON, Yang R, Grenfell BT, Pybus OG, Dye C. An investigation of transmission control measures during the first 50 days of the COVID-19 epidemic in China. Science (80-) 2020;368:eabb6105. doi: 10.1126/science.abb6105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
