Genome Sequence of Synechococcus sp. Strain LA31, Isolated from a Temperate Estuary
- PMID: 35195452
- PMCID: PMC8928756
- DOI: 10.1128/mra.00775-21
Genome Sequence of Synechococcus sp. Strain LA31, Isolated from a Temperate Estuary
Abstract
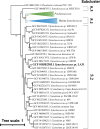
Cluster 5 Synechococcus species are widely acknowledged for their broad distribution and biogeochemical importance. In particular, subcluster 5.2 strains inhabit freshwater, estuarine, and marine environments but are understudied, compared to other subclusters. Here, we present the genome for Synechococcus sp. strain LA31, a strain that was recently isolated from Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island, USA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lee MD, Ahlgren NA, Kling JD, Walworth NG, Rocap G, Saito MA, Hutchins DA, Webb EA. 2019. Marine Synechococcus isolates representing globally abundant genomic lineages demonstrate a unique evolutionary path of genome reduction without a decrease in GC content. Environ Microbiol 21:1677–1686. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.14552. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen F, Wang K, Kan J, Bachoon DS, Lu J, Lau S, Campbell L. 2004. Phylogenetic diversity of Synechococcus in the Chesapeake Bay revealed by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase (RuBisCO) large subunit gene (rbcL) sequences. Aquat Microb Ecol 36:153–164. doi:10.3354/ame036153. - DOI
-
- Flombaum P, Gallegos JL, Gordillo RA, Rincón J, Zabala LL, Jiao N, Karl DM, Li WKW, Lomas MW, Veneziano D, Vera CS, Vrugt JA, Martiny AC. 2013. Present and future global distributions of the marine cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:9824–9829. doi:10.1073/pnas.1307701110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guillard RRL. 1975. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates, p 29–60. In Smith WL, Chanley MH (ed), Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Plenum Press, New York, NY.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
