Astrocyte-neuron crosstalk through Hedgehog signaling mediates cortical synapse development
- PMID: 35196485
- PMCID: PMC8962654
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110416
Astrocyte-neuron crosstalk through Hedgehog signaling mediates cortical synapse development
Abstract
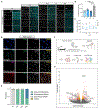
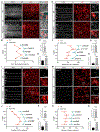
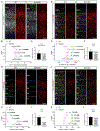
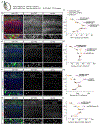
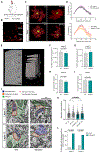
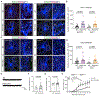
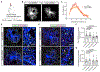
Neuron-glia interactions play a critical role in the regulation of synapse formation and circuit assembly. Here we demonstrate that canonical Sonic hedgehog (Shh) pathway signaling in cortical astrocytes acts to coordinate layer-specific synaptic connectivity. We show that the Shh receptor Ptch1 is expressed by cortical astrocytes during development and that Shh signaling is necessary and sufficient to promote the expression of genes involved in regulating synaptic development and layer-enriched astrocyte molecular identity. Loss of Shh in layer V neurons reduces astrocyte complexity and coverage by astrocytic processes in tripartite synapses; conversely, cell-autonomous activation of Shh signaling in astrocytes promotes cortical excitatory synapse formation. Furthermore, Shh-dependent genes Lrig1 and Sparc distinctively contribute to astrocyte morphology and synapse formation. Together, these results suggest that Shh secreted from deep-layer cortical neurons acts to specialize the molecular and functional features of astrocytes during development to shape circuit assembly and function.
Keywords: Lrig1; Sonic hedgehog; Sparc; astrocytes; cortical circuits; neuron-glia interaction; synapse formation.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

