YAP and TAZ in Vascular Smooth Muscle Confer Protection Against Hypertensive Vasculopathy
- PMID: 35196875
- PMCID: PMC8939708
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.317365
YAP and TAZ in Vascular Smooth Muscle Confer Protection Against Hypertensive Vasculopathy
Abstract
Background: Hypertension remains a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, but the underlying mechanisms are not well understood. We hypothesize that appropriate mechanotransduction and contractile function in vascular smooth muscle cells are crucial to maintain vascular wall integrity. The Hippo pathway effectors YAP (yes-associated protein 1) and TAZ (WW domain containing transcription regulator 1) have been identified as mechanosensitive transcriptional coactivators. However, their role in vascular smooth muscle cell mechanotransduction has not been investigated in vivo.
Methods: We performed physiological and molecular analyses utilizing an inducible smooth muscle-specific YAP/TAZ knockout mouse model.
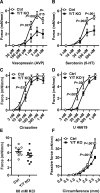
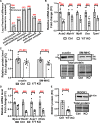
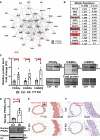
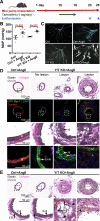
Results: Arteries lacking YAP/TAZ have reduced agonist-mediated contraction, decreased myogenic response, and attenuated stretch-induced transcriptional regulation of smooth muscle markers. Moreover, in established hypertension, YAP/TAZ knockout results in severe vascular lesions in small mesenteric arteries characterized by neointimal hyperplasia, elastin degradation, and adventitial thickening.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates a protective role of YAP/TAZ against hypertensive vasculopathy.
Keywords: adventitia; compliance; hyperplasia; muscle; neointima; smooth; vascular.
Figures



References
-
- Mulvany MJ, Baumbach GL, Aalkjaer C, Heagerty AM, Korsgaard N, Schiffrin EL, Heistad DD. Vascular remodeling. Hypertension. 1996; 28:505–506 - PubMed
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE, Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, DePalma SM, Gidding S, Jamerson KA, Jones DW, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2018; 138:e426–e483. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000597 - PubMed
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006; 367:1747–1757. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68770-9 - PubMed
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff DC, Murphy TP, Toto RD, White A, Cushman WC, White W, Sica D, et al. ; American Heart Association Professional Education Committee. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation. 2008; 117:e510–e526. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.189141 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

