Comparison of MynxGrip vascular closure device and manual compression for closure after femoral access angiography: a randomized controlled trial: the closure devices used in every day practice study, CLOSE-UP III trial
- PMID: 35196986
- PMCID: PMC8864788
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-022-02512-0
Comparison of MynxGrip vascular closure device and manual compression for closure after femoral access angiography: a randomized controlled trial: the closure devices used in every day practice study, CLOSE-UP III trial
Abstract
Background: Complications related to femoral artery access for coronary angiography (CAG) is a safety concern. Vascular closure devices (VCDs) have been developed to reduce the rate of complications after femoral artery access. We compared the safety and efficacy of the MynxGrip VCD versus manual compression (MC) after femoral access CAG in a randomized controlled trial.
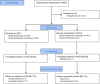
Methods: The study was a randomized, single center, non-blinded, two-arm non-inferiority trial. The study was stopped prematurely because of low inclusion rate.
Results: We randomized 869 patients to closure with the MynxGrip VCD or MC and 865 entered analyses. The incidence of the primary endpoint of major adverse vascular events (MAVE) after 30 days was 1.2% in the MynxGrip group and 0% in the MC group (p = 0.06). The median time to hemostasis was 4 [3:5] minutes and 10 [7:11] minutes in the MynxGrip group and MC group, respectively (p < 0.0001). The corresponding median times to mobilization was 73 [65:87] minutes and 76 [70:88] minutes (p = 0.01).
Conclusions: MAVE was rare after closure of femoral arterial access by both the MynxGrip VCD and MC. We found a numerical difference in favour of MC but this did not reach statistical significance. Time to hemostasis was shorter in the MynxGrip group when compared to the MC group.
Trial registration: The study was approved by the local medical ethics committee and registered at clinicaltrials.org (ClinicalTrials identifier: NCT02237430 11/09/2014).
Keywords: Access site; Bleeding; Femoral; Vascular access closure device.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Nikolsky E, Mehran R, Halkin A, Aymong ED, Mintz GS, Lasic Z, et al. Vascular complications associated with arteriotomy closure devices in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary procedures: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:1200–1209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

