YTHDF1 promotes breast cancer progression by facilitating FOXM1 translation in an m6A-dependent manner
- PMID: 35197112
- PMCID: PMC8867832
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-022-00759-w
YTHDF1 promotes breast cancer progression by facilitating FOXM1 translation in an m6A-dependent manner
Abstract
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most common post-transcriptional modification at the RNA level. However, the exact molecular mechanisms of m6A epigenetic regulation in breast cancer remain largely unknown and need to be fully elucidated.
Methods: The integrating bioinformatics analyses were used to screen clinical relevance and dysregulated m6A "reader" protein YTHDF1 in breast cancer from TCGA databases, which was further validated in a cohort of clinical specimens. Furthermore, functional experiments such as the CCK-8 assay, EdU assay, wound healing assay, transwell invasion assay and cell cycle assay were used to determine the biological role of YTHDF1 in breast cancer. RIP, m6A-IP, and CLIP assays were used to find the target of YTHDF1 and further verification by RT-qPCR, western blot, polysome profiling assay. The protein-protein interaction between YTHDF1 and FOXM1 was detected via co-immunoprecipitation.
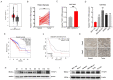
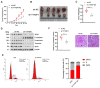
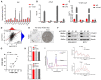
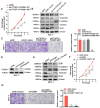
Results: Our study showed that YTHDF1 was overexpressed in breast cancer cells and clinical tissues specimens. At the same time, the high expression level of YTHDF1 was positively correlated with tumor size, lymph node invasion, and distant metastasis in breast cancer patients. YTHDF1 depletion repressed the proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) and induced G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. We also demonstrated that FOXM1 is a target of YTHDF1. Through recognizing and binding to the m6A-modified mRNA of FOXM1, YTHDF1 accelerated the translation process of FOXM1 and promoted breast cancer metastasis. Whereas overexpression of FOXM1 in breast cancer cells partially counteracted the tumor suppressed effects caused by YTHDF1 silence, which further verified the regulatory relationship between YTHDF1 and FOXM1.
Conclusion: Our study reveals a novel YTHDF1/FOXM1 regulatory pathway that contributes to metastasis and progression of breast cancer, suggesting that YTHDF1 might be applied as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target. That also advances our understanding of the tumorigenesis for breast cancer from m6A epigenetic regulation.
Keywords: Breast cancer; EMT; FOXM1; YTHDF1; m6A.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The potential role of m6A reader YTHDF1 as diagnostic biomarker and the signaling pathways in tumorigenesis and metastasis in pan-cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jan 28;9(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01321-4. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36707507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KIAA1429 increases FOXM1 expression through YTHDF1-mediated m6A modification to promote aerobic glycolysis and tumorigenesis in multiple myeloma.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Jul 26;40(1):58. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09904-2. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39060874 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation recognition protein YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 1 (YTHDF1) regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma by regulating m6A level of CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit 7 (CNOT7).Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):5236-5250. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2037381. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35156522 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α-induced expression of m6A reader YTHDF1 drives hypoxia-induced autophagy and malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting ATG2A and ATG14 translation.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Feb 23;6(1):76. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00453-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33619246 Free PMC article.
-
The roles and mechanisms of the m6A reader protein YTHDF1 in tumor biology and human diseases.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Nov 4;26:1270-1279. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.10.023. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34853726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stabilization of IGF2BP1 by USP10 promotes breast cancer metastasis via CPT1A in an m6A-dependent manner.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jan 1;19(2):449-464. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.76798. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36632454 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine reader YTHDF family in biological processes: Structures, roles, and mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 14;14:1162607. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1162607. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36999016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential role of m6A reader YTHDF1 as diagnostic biomarker and the signaling pathways in tumorigenesis and metastasis in pan-cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jan 28;9(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01321-4. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36707507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 13;24(14):11386. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411386. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511145 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Roles of m6A RNA Modification in Translational Regulation in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 11;23(16):8971. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168971. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012237 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fu Y, et al. Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m6A RNA methylation. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(5):293–306. - PubMed
-
- Zaccara S, Ries RJ, Jaffrey SR. Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(10):608–624. - PubMed
-
- Ma Z, Ji J. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification in cancer stem cells. Stem Cells. 2020;38(12):1511–1519. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

