Waiting for JAK inhibitor safety data
- PMID: 35197363
- PMCID: PMC8867353
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002236
Waiting for JAK inhibitor safety data
Abstract
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently added a new 'black box warning' on all currently approved Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors indicated for the treatment of arthritis and other inflammatory conditions based on results from the ORAL Surveillance study of tofacitinib versus tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. This is a warning difficult to ignore because the data, being from a randomised controlled trial, are of high fidelity and hard to reproach. It is especially problematic because safety data for all the other JAK inhibitors will be pending for several years. So how might we proceed, without being bound by our stasis? The lack of absolute certainty seems to require a pragmatic approach to the routine care use of JAK inhibitors. The patients who were at greatest risk were older and had other risk factors for the corresponding adverse events, in keeping with effect modification. This highlights the need to focus on risk stratification when tailoring therapy. In this viewpoint, we propose a simple illustration to guide clinical decision-making. First, identify general risk factors for venous thromboembolic event (VTE), major adverse cardiac event (MACE) and cancer (age>65 years and smoking) and whether there is a previous history of VTE, MACE or cancer. Then, evaluate risk based on the number of other risk factors for VTE and the number of other risk factors for MACE. Ultimately, 'treat-to-target' will in the end always be 'treat-to-agreement'. As we have done in the past, and will do in the future, the optimal treatment strategy will have to be tailored based on individual patient risk factors and preferences in a shared-decision process.
Keywords: antirheumatic agents; arthritis, psoriatic; arthritis, rheumatoid; spondylitis, ankylosing; therapeutics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: TWK: Speaking fees from Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, UCB and AbbVie. Consultancy fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Gilead. Research grants from Gilead. Co-founder and clinical developer in iBio Tech ApS. BG: Research grants from Pfizer, BMS, AbbVie. BD: Speaking fees from Pfizer, Novartis and AbbVie. Consultancy fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Novartis, Gilead, Eli Lilly. Research grants: Gilead and AbbVie. PCR reports personal fees from AbbVie, Atom Biosciences, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Kukdong, Novartis, UCB, Roche, Pfizer; meeting attendance support from BMS, Pfizer and UCB; and grant funding from Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB Pharma.
Figures
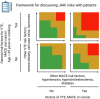
References
-
- Administration UFaD . FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions, 2021.
-
- Agency EM . Xeljanz (tofacitinib) summary of product characteristics, 2021. Available: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/xeljanz-epar-... [Accessed 2 Feb 2022].
-
- Administration USFD . Xeljanz (tofacitinib) highlights of prescribing information, 2021. Available: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/203214s028,208... [Accessed 2 Feb 2022].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
