Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Spirulina platensis extracts and biogenic selenium nanoparticles against selected pathogenic bacteria and fungi
- PMID: 35197787
- PMCID: PMC8848030
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.046
Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Spirulina platensis extracts and biogenic selenium nanoparticles against selected pathogenic bacteria and fungi
Abstract
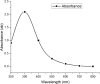
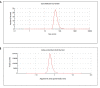
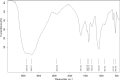
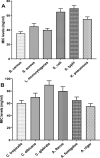
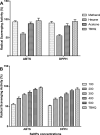
This study investigated the antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of three Spirulina extracts (methanol, acetone, and hexane) and the biological selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) fabricated by Bacillus subtilis AL43. The results showed that Spirulina extracts exhibited antimicrobial activity against tested pathogens. Besides, Spirulina extracts significantly scavenged ABTS and DPPH radicals in a dose-dependent manner. The methanolic extract had higher total phenolic content, antimicrobial activity, and antioxidant activity than other extracts. The selenium nanoparticles were synthesized by Bacillus subtilis AL43 under aerobic conditions and were characterized as spherical, crystalline with a size of 65.23 nm and a net negative charge of -22.7. We evidenced that SeNPs possess considerable antimicrobial activity against three gram-positive, three gram-negative bacteria, and three strains from both Candida sp. and Aspergillus sp. Moreover, SeNPs were able to scavenge ABTS and DPPH radicals in a dose-dependent manner. An association was found between the total phenolic content of Spirulina and SeNPs and their biological activities. Our results indicate that Spirulina and SeNPs with significant antimicrobial and antioxidant activities seem to be successful candidates for safe and reliable medical applications.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Antioxidant; Bacillus subtilis; Biogenic SeNPs; Green nanotechnology; Spirulina platensis.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Abbas H.S., Abou Baker D.H., Ahmed E.A. Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial efficiency of selenium nanoparticles biosynthesized by Spirulina platensis. Arch. Microbiol. 2021;203:523–532. - PubMed
-
- Abd El-Hack M.E., Abdelnour S.A., Abd El-Moneim A.E., Arif M., Khafaga A., Shaheen H., Samak D., Swelum A.A. Putative impacts of phytogenic additives to ameliorate lead toxicity in animal feed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019;26:23209–23218. - PubMed
-
- Abd El-Hack M.E., El-Saadony M.T., Shafi M.E., Alshahrani O.A., Saghir S.A., Al-Wajeeh A.S., Al-Shargi O.Y., Taha A.E., Mesalam N.M., Abdel-Moneim A.-M.-E. Prebiotics can restrict Salmonella populations in poultry: a review. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021;19:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Abd El-Hack M.E., El-Saadony M.T., Shafi M.E., Zabermawi N.M., Arif M., Batiha G.E., Khafaga A.F., Abd El-Hakim Y.M., Al-Sagheer A.A. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of chitosan and its derivatives and their applications: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020;1(164):2726–2744. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

