The Effect of Abnormal Regional Homogeneity and Spontaneous Low-Frequency Brain Activity on Lower Cognitive Ability: A Cross-Sectional Study on Postoperative Children With Tetralogy of Fallot
- PMID: 35197816
- PMCID: PMC8858977
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.685372
The Effect of Abnormal Regional Homogeneity and Spontaneous Low-Frequency Brain Activity on Lower Cognitive Ability: A Cross-Sectional Study on Postoperative Children With Tetralogy of Fallot
Abstract
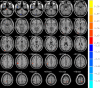
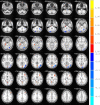
Despite intracardiac malformation correction, children with Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) may still suffer from brain injury. This cross-sectional study was primarily designed to determine the relationship between blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) signal changes after surgery and cognition in school-aged children with TOF. To evaluate the differences between TOF children (n = 9) and healthy children (n = 9), resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Chinese revised edition (WISC-CR) were conducted in this study. The results showed that TOF children had a lower full-scale intelligence quotient (FSIQ, 95.444 ± 5.354, p = 0.022) and verbal intelligence quotient (VIQ, 92.444 ± 4.708, p = 0.003) than healthy children (FSIQ = 118.500 ± 4.330;VIQ = 124.250 ± 4.404), and that significant differences in regional homogeneity (ReHo) and amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) existed between the two groups. Besides, VIQ had significantly positive correlations with the decreased ALFF value of the middle inferior occipital gyrus (MIOG, beta = 0.908, p = 0.012) after fully adjusting for all covariates. In addition, elevated ReHo values of the left and right precuneus were positively related to ALFF in the MIOG. This study revealed that brain injury substantially influences neural activity and cognition in postoperative TOF children, providing direct evidence of an association between BOLD signal changes and the VIQ and prompting further attention to language development in TOF children.
Keywords: ALFF; ReHo; Tetralogy of Fallot; VIQ; brain injury; cognition.
Copyright © 2022 Ma, Hu, Liu, Pu, Zuo, Hu, Yang, Chen, Xie, Cun, Liu, Yang and Mo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer Y-CC declared a shared affiliation, though no other collaboration, with the authors to the handling Editor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in Cortical Thickness Are Associated With Cognitive Ability in Postoperative School-Aged Children With Tetralogy of Fallot.Front Neurol. 2020 Jul 17;11:691. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00691. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32765405 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of spontaneous brain activity in systematic lupus erythematosus patients without neuropsychiatric symptoms: A resting-functional MRI study.Lupus. 2021 Oct;30(11):1781-1789. doi: 10.1177/09612033211033984. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Lupus. 2021. PMID: 34620007
-
Disrupted neural activity in unilateral vascular pulsatile tinnitus patients in the early stage of disease: evidence from resting-state fMRI.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Jun 3;59:91-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.01.013. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25645870
-
Local synchronization and amplitude of the fluctuation of spontaneous brain activity in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a resting-state fMRI study.Neurosci Bull. 2013 Oct;29(5):603-13. doi: 10.1007/s12264-013-1353-8. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Neurosci Bull. 2013. PMID: 23861089 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant Spontaneous Brain Activity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment and concomitant Lacunar Infarction: A Resting-State Functional MRI Study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;50(4):1243-54. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150622. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 26836013
Cited by
-
Atoh1 mediated disturbance of neuronal maturation by perinatal hypoxia induces cognitive deficits.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 11;7(1):1121. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06846-7. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39261625 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative serum cortisone levels are associated with cognition in preschool-aged children with tetralogy of Fallot after corrective surgery: new evidence from human populations and mice.World J Pediatr. 2024 Feb;20(2):173-184. doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00754-2. Epub 2023 Sep 22. World J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 37737505 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

