How Social Experiences Affect Interpretation Bias Among Individuals With Non-clinical Depression: The Role of Ostracism
- PMID: 35197878
- PMCID: PMC8860160
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.819143
How Social Experiences Affect Interpretation Bias Among Individuals With Non-clinical Depression: The Role of Ostracism
Abstract
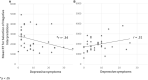
Background: Extensive knowledge and research indicate that interpretation bias is very common among individuals with sub-clinical and clinical levels of depression. Nevertheless, little is known about the role of social experiences in enhancing interpretation bias. Given the major relevance of social experiences in the context of depression, the present study investigated the role of potential interactions between social experiences and levels of depression symptoms in the interpretation of ambiguous information.
Method: Seventy participants underwent a laboratory controlled manipulation either of social ostracism or of overinclusion. Participants completed a computerized task that measured both direct and indirect interpretation bias and reported their level of depression symptoms.
Results: The findings show that ostracism enhanced interpretation bias when symptom levels were higher, while overinclusion did not. This interaction effect between social ostracism and symptom level was found both for direct and for indirect interpretation bias.
Conclusion: Whereas previous research showed the existence of interpretation bias among people with symptoms of depression, the present study expands previous knowledge by shedding light on the conditions under which interpretation bias emerges, suggesting that ostracism enhances negative interpretation of ambiguous information when levels of depression symptoms are higher.
Keywords: Cyberball task; cognitive bias; depression; interpretation bias; ostracism; social cognition.
Copyright © 2022 Bar-Sella, Richter, Zilcha-Mano and Okon-Singer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Beck AT, Clark DA. Anxiety and depression: An information processing perspective. Anxiety Res. (1988) 1:23–36. 10.1080/10615808808248218 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

