Efficacy of Dimethyl Trisulfide on the Suppression of Ring Rot Disease Caused by Botryosphaeria dothidea and Induction of Defense-Related Genes on Apple Fruits
- PMID: 35197948
- PMCID: PMC8859264
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.796167
Efficacy of Dimethyl Trisulfide on the Suppression of Ring Rot Disease Caused by Botryosphaeria dothidea and Induction of Defense-Related Genes on Apple Fruits
Abstract
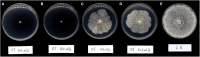
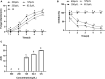
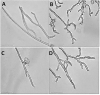
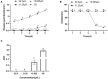
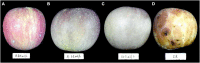
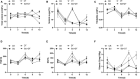
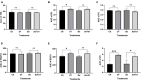
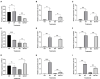
Apple ring rot caused by Botryosphaeria dothidea is prevalent in main apple-producing areas in China, bringing substantial economic losses to the growers. In the present study, we demonstrated the inhibitory effect of dimethyl trisulfide (DT), one of the main activity components identified in Chinese leek (Allium tuberosum) volatile, on the apple ring rot on postharvest fruits. In in vitro experiment, 250 μL/L DT completely suppressed the mycelia growth of B. dothidea. In in vivo experiment, 15.63 μL/L DT showed 97% inhibition against the apple ring rot on postharvest fruit. In addition, the soluble sugar content, vitamin C content, and the soluble sugar/titratable acidity ratio of the DT-treated fruit were significantly higher than those of the control fruit. On this basis, we further explored the preliminary underlying mechanism. Microscopic observation revealed that DT seriously disrupted the normal morphology of B. dothidea. qRT-PCR determination showed the defense-related genes in DT-treated fruit were higher than those in the control fruit by 4.13-296.50 times, which showed that DT inhibited apple ring rot on postharvest fruit by suppressing the growth of B. dothidea, and inducing the defense-related genes in apple fruit. The findings of this study provided an efficient, safe, and environment-friendly alternative to control the apple ring rot on apple fruit.
Keywords: Allium tuberosum; Botryosphaeria dothidea; biocontrol; defensive genes; fruit quality.
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Duan, Liu, Fu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bai S., Dong C., Zhu J., Zhang Y., Dai H. (2015). Identification of a xyloglucan-specific endo-(1-4)-beta-D-glucanase inhibitor protein from apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) as a potential defense gene against Botryosphaeria dothidea. Plant Sci. 231 11–19. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.11.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balamanikandan T., Balaji S., Pandiarajan J. (2015). Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using onion (Allium cepa) extract and their antibacterial and antifungal activity. World Appl. Sci. J. 33 939–943. 10.5829/idosi.wasj.2015.33.06.9525 - DOI
-
- Bhattacharya S., Sen D., Bhattacharjee C. (2019). In vitro antibacterial effect analysis of stabilized PEGylated allicin-containing extract from Allium sativum in conjugation with other antibiotics. Process Biochem. 87 221–231. 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.09.025 - DOI
-
- Dai D. J., Wang H. D., Wang Y. P., Zhang C. Q. (2017). Management of Chinese hickory (Carya cathayensis) trunk canker through effective fungicide application programs and baseline sensitivity of Botryosphaeria dothidea to trifloxystrobin. Austral. Plant Pathol. 46 75–82. 10.1007/s13313-017-0465-4 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

