More on the invisibility of chronic kidney disease… and counting
- PMID: 35198154
- PMCID: PMC8690216
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfab240
More on the invisibility of chronic kidney disease… and counting
Abstract
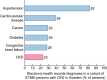
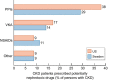
Lack of awareness of a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in patients and physicians is a major contributor to fueling the CKD pandemic by also making it invisible to researchers and health authorities. This is an urgent matter to tackle if dire predictions of future CKD burden are to be addressed. CKD is set to become the fifth-leading global cause of death by 2040 and the second-leading cause of death before the end of the century in some countries with long life expectancy. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) illustrated this invisibility: only after the summer of 2020 did it become clear that CKD was a major driver of COVID-19 mortality, both in terms of prevalence as a risk factor and of the risk conferred for lethal COVID-19. However, by that time the damage was done: news outlets and scientific publications continued to list diabetes and hypertension, but not CKD, as major risk factors for severe COVID-19. In a shocking recent example from Sweden, CKD was found to be diagnosed in just 23% of 57 880 persons who fulfilled diagnostic criteria for CKD. In the very same large cohort, diabetes or cancer were diagnosed in 29% of persons, hypertension in 82%, cardiovascular disease in 39% and heart failure in 28%. Thus, from the point of view of physicians, patients and health authorities, CKD was the least common comorbidity in persons with CKD, ranking sixth, after other better-known conditions. One of the consequences of this lack of awareness was that nephrotoxic medications were more commonly prescribed in patients with CKD who did not have a diagnosis of CKD. Low awareness of CKD may also fuel concepts such as the high prevalence of hypertensive nephropathy when CKD is diagnosed after the better-known condition of hypertension.
Keywords: awareness; chronic kidney disease; hypertensive nephropathy; misdiagnosis; nephrotoxic drugs; nephrotoxicity.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures

Comment in
-
RICORS2040: the need for collaborative research in chronic kidney disease.Clin Kidney J. 2021 Sep 23;15(3):372-387. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfab170. eCollection 2022 Mar. Clin Kidney J. 2021. PMID: 35211298 Free PMC article.
-
Use of nephrotoxic medications in adults with chronic kidney disease in Swedish and US routine care.Clin Kidney J. 2021 Oct 29;15(3):442-451. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfab210. eCollection 2022 Mar. Clin Kidney J. 2021. PMID: 35296039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jager KJ, Kovesdy C, Langham Ret al. . A single number for advocacy and communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2019; 34: 1803–1805 - PubMed
-
- Ortiz A, Asociación Información Enfermedades Renales Genéticas, European Kidney Patients' Federation et al. RICORS2040: the need for collaborative research in chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J 2021; 10.1093/ckj/sfab170 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

