Belantamab mafodotin associated corneal microcyst-like epithelial changes
- PMID: 35198816
- PMCID: PMC8851095
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2022.101392
Belantamab mafodotin associated corneal microcyst-like epithelial changes
Abstract
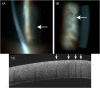
Purpose: To report a case of bilateral corneal microcyst-like epithelial changes associated with belantamab mafodotin (belamaf) therapy.
Observations: A 70-year-old man with refractory multiple myeloma was placed on belamaf, a recently FDA-approved treatment for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. He developed decreased visual acuity and bilateral corneal microcyst-like peripheral epithelial changes. Belamaf was withheld.Anterior segment OCT showed intra-epithelial opacities at various depths. After resolution of corneal changes and recovery of vision, belamaf was restarted. The patient underwent two additional treatments, each time with recurrence of diffuse microcyst-like corneal epithelial changes. It took a total of 8, 11.5 and 17 weeks after each respective infusion for the microcyst-like epithelial changes to resolve. This suggested a longer recovery time after each subsequent infusion.
Conclusions and importance: The care for patients on belamaf requires the collaboration of eye care providers and hematologists-oncologists to assess for ocular adverse effects and adjust treatment as necessary. Further study is needed to illustrate the mechanism of corneal microcyst-like epithelial changes and its effects on limbal stem cells.
Keywords: Belantamab mafodotin; Cornea; Drug adverse effects.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The following authors have no financial disclosures: K·C., R.P. S.L. is an external consultant for GlaxoSmithKline LLC.
Figures
References
-
- Markham A. Belantamab mafodotin: first approval. Drugs. 2020;80(15):1607–1613. - PubMed
-
- Lonial S., Lee H.C., Badros A., et al. Belantamab mafodotin for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (DREAMM-2): a two-arm, randomised, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(2):207–221. - PubMed
-
- Zhao H., Atkinson J., Gulesserian S., et al. Modulation of macropinocytosis-mediated internalization decreases ocular toxicity of antibody-drug conjugates. Cancer Res. 2018 Apr 15;78(8):2115–2126. - PubMed
-
- Lee B.A., Lee M.S., Maltry A.C., et al. Clinical and histological characterization of toxic keratopathy from depatuxizumab mafodotin (ABT-414), an antibody-drug conjugate. Cornea. 2021 Sep 1;40(9):1197–1200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

