Influence of Moringa (Moringa oleifera) enriched ice creams on rats' brain: Exploring the redox and cholinergic systems
- PMID: 35198996
- PMCID: PMC8850994
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.01.021
Influence of Moringa (Moringa oleifera) enriched ice creams on rats' brain: Exploring the redox and cholinergic systems
Abstract
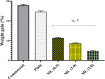
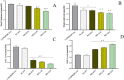
The broad application of Moringa oleifera leaves in the treatment of numerous diseases is prevalent globally where it extends to the management of diabetes, hypertension, inflammation, hypercholesterolemia and neurodegenerative diseases. This study provides findings on the role of Moringa oleifera leaves (MO) [MO leaves] formulated ice creams on brain cholinergic enzymes [acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE)], antioxidant enzymes, glycemic index and blood lipid profile of rats. Thirty (30) adult male rats acclimatized for 2 weeks were divided into five groups: Group 1 rats received commercial ice cream, Group 2 rats were received plain ice-cream, Group 3, 4 and 5 received 0.5 g, 1.0 g and 2.0 g of MO-formulated ice creams. Rats were fed on normal pellets and exposed to ice creams produced from whipping cream, skimmed milk and Moringa oleifera leaves for 30 consecutive days. Following administration, results from this study revealed that rats that received Moringa formulated ice-creams had reduced brain butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) enzymes activities, glycemic index (GI), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels and significantly increased high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) level in the plasma while revealing elevated brain antioxidant status (Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and Catalase (CAT)) when compared against rats consuming commercial ice creams. Therefore, results from this study attests to the intake of ice creams made from blends of Moringa leaves in the reduction of rats' body weight, glycemic index and lipid profile (TC, TG, LDL-C), inhibition of brain cholinergic enzymes (AChE and BChE) while increasing brain antioxidant enzymes activities (SOD and CAT).
Keywords: Brain antioxidants; Cholinergic enzymes; Glycemic indices; Ice creams; Moringa oleifera.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Adedayo B., Okeke B.M, Oyeleye S.I, Oboh G. Effects of boiling on the estimated Glycemic Index (eGI) and α- amylase/α-glucosidase inhibitory properties of two Bitter Yam (Dioscorea dumetorum) spp. Biokemistri. 2018;30:21–31.
-
- Akinyemi A.J., Oboh G., Oyeleye S.I., Ogunsuyi O. Antiamnestic effect of curcumin in combination with donepezil, an anti-cholinesterase drug: involvement of cholinergic system. Neurotox. Res. 2017;31(4):560–569. - PubMed
-
- Anil K.A., Singh H. Recent advances in microencapsulation of probiotics for industrial applications and targeted delivery. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007;8:5 240–251.
-
- Assini J.M., Mulvihill E.E., Huf M.W. Citrus favonoids and lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2013;24(1):34–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

