Covid-19, social restrictions, and mental distress among young people: a UK longitudinal, population-based study
- PMID: 35199336
- PMCID: PMC9114888
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpp.13586
Covid-19, social restrictions, and mental distress among young people: a UK longitudinal, population-based study
Abstract
Background: Adolescence is a critical period for social and emotional development. We sought to examine the impacts of Covid-19 and related social restrictions and school closures on adolescent mental health, particularly among disadvantaged, marginalised, and vulnerable groups.
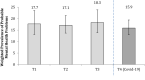
Methods: We analysed four waves of data - 3 pre-Covid-19 (2016-2019) and 1 mid-Covid-19 (May-Aug 2020; n, 1074; 12-18 years old, >80% minority ethnic groups, 25% free school meals) from REACH (Resilience, Ethnicity, and AdolesCent Mental Health), an adolescent cohort based in inner-London, United Kingdom. Mental health was assessed using validated measures at each time point. We estimated temporal trends in mental distress and examined variations in changes in distress, pre- to mid-Covid-19, by social group, and by pre- and mid-pandemic risks.
Results: We found no evidence of an overall increase in mental distress midpandemic (15.9%, 95% CI: 13.0, 19.4) compared with prepandemic (around 18%). However, there were variations in changes in mental distress by subgroups. There were modest variations by social group and by pre-Covid risks (e.g., a small increase in distress among girls (b [unstandardised beta coefficient] 0.42 [-0.19, 1.03]); a small decrease among boys (b - 0.59 [-1.37, 0.19]); p for interaction .007). The most notable variations were by midpandemic risks: that is, broadly, increases in distress among those reporting negative circumstances and impacts (e.g., in finances, housing, social support and relationships, and daily routines) and decreases in distress among those reporting positive impacts.
Conclusions: We found strong evidence that mental distress increased among young people who were most negatively impacted by Covid-19 and by related social restrictions during the first lockdown in the United Kingdom.
Keywords: Covid-19; adolescence; cohort; mental distress.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health.
Figures
References
-
- Ancold, A. , & Stephen, C. (1995). Development of a short questionnaire for use in epidemiological studies of depression in children and adolescents. Age (years), 6, 237–249.
-
- Bor, W. , Dean, A.J. , Najman, J. , & Hayatbakhsh, R. (2014). Are child and adolescent mental health problems increasing in the 21st century? A systematic review. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 48, 606–616. - PubMed
-
- Collishaw, S. (2015). Annual research review: Secular trends in child and adolescent mental health. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 56, 370–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical