Human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-15a-5p possess therapeutic effects on Wilms tumor via regulating septin 2
- PMID: 35200105
- PMCID: PMC8973990
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2037379
Human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-15a-5p possess therapeutic effects on Wilms tumor via regulating septin 2
Abstract
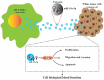
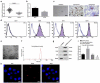
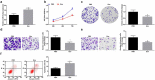
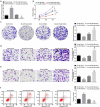
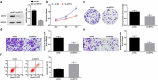
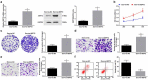
The exact mechanism of miR-15a-5p shuttled by human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (hUC-MSCs-Exo) in Wilms tumor (WT) was estimated. WT tissues were collected clinically. miR-15a-5p and septin 2 (SEPT2) expression levels were examined in tissues . hUC-MSCs-Exo were transfected with miR-15a-5p-related oligonucleotides and co-cultured with WT cells (G-401). In addition, SEPT2 loss-of-function was performed in G-401 cells. The biological functions of G-401 cells after treatments were evaluated. Moreover, tumor formation tests further assessed the role of exosomal miR-15a-5p in WT. The miR-15a-5p level was lower and the SEPT2 level was higher in WT. hUC-MSCs-Exo impaired the biological functions of G-401 cells. hUC-MSCs-Exo carried upregulated miR-15a-5p into G-401 cells, thereby lessening the tumorigenic properties of G-401 cells. Inhibition of SEPT2 suppressed the biological function of WT cells and upregulated SEPT2 reversed hUC-MSCs-Exo-mediated inhibition of G-401 cell growth. The tumorigenicity of G-401 cells in mice was impaired by hUC-MSCs-Exo overexpressing miR-15a-5p. The data prove that miR-15a-5p shuttled by hUC-MSCs-Exo negatively regulates SEPT2 expression, and disrupts WT cell growth in vivo and in vitro.
Keywords: MicroRNA-15a-5p; Wilms tumor; human umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes; septin 2.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
microRNA-140-5p from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-released exosomes suppresses preeclampsia development.Funct Integr Genomics. 2022 Oct;22(5):813-824. doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00848-6. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Funct Integr Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35484307
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibit liver fibrosis via the microRNA-148a-5p/SLIT3 axis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Dec;125(Pt A):111134. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111134. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37918086
-
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-exosomal miR-627-5p ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by repressing FTO expression.Hum Cell. 2021 Nov;34(6):1697-1708. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00593-1. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 34410623
-
The therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived exosomes in the ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Apr 1;13(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02811-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35365226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of the anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic potential of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in experimental models of liver regeneration.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Sep 20;51(1):999. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09929-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39302506
Cited by
-
Unveiling the multifaceted roles of microRNAs in extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells: implications in tumor progression and therapeutic interventions.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 5;15:1438177. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1438177. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39161894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived exosomes and genitourinary cancers: A mini review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 4;10:1115786. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1115786. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36684446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential use of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes as microRNAs delivery systems in different diseases.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jan 23;21(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-01017-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36690996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro evaluation of 3D-printed conductive chitosan-polyaniline scaffolds with exosome release for enhanced angiogenesis and cardiomyocyte protection.RSC Adv. 2025 May 20;15(21):16826-16844. doi: 10.1039/d5ra02940f. eCollection 2025 May 15. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40395791 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miR-486-5p inhibit glycolysis and cell stemness in colorectal cancer by targeting NEK2.BMC Cancer. 2024 Nov 6;24(1):1356. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13086-9. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39506654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Millar AJW, Cox S, Davidson A.. Management of bilateral Wilms tumours. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017;33(7):737–745. - PubMed
-
- Pater L, Melchior P, Rübe C, et al. Wilms tumor. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2021;68(Suppl 2):e28257. - PubMed
-
- Friedman AD. Wilms tumor. Pediatr Rev. 2013;34(7):328–330. discussion 330. - PubMed
-
- Parsons LN. Wilms tumor: challenges and newcomers in prognosis. Surg Pathol Clin. 2020;13(4):683–693. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
