Development of a Rapid Gold Nanoparticle Immunochromatographic Strip Based on the Nanobody for Detecting 2,4-DichloRophenoxyacetic Acid
- PMID: 35200344
- PMCID: PMC8869386
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12020084
Development of a Rapid Gold Nanoparticle Immunochromatographic Strip Based on the Nanobody for Detecting 2,4-DichloRophenoxyacetic Acid
Abstract
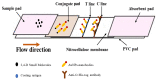
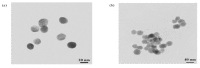
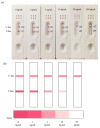
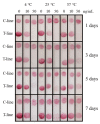
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) is a systemic conductive herbicide widely used across the world. With the large-scale and continuous use of 2,4-D, its possible harm to the environment and non-target organisms has attracted increasing attention, and the construction of a stable rapid on-site detection method is particularly important. In order to achieve on-site rapid detection of 2,4-D, we developed a gold nanoparticle immunochromatographic strip method with the visual elimination value was 50 ng/mL, and a quantitative detection limit of 11 ng/mL based on a nanobody. By combing with the color snap, the immunochromatographic strip could quantitatively analyze the amounts of 2,4-D. Meanwhile, a colorimetric card based on the true color of the test strips was developed for the qualitative analysis of 2,4-D on-site. The samples (water, fruits and vegetables) with and without 2,4-D were detected by the immunochromatographic strips, and the results showed the accuracy and reliability. Thus, this assay is a rapid and simple on-site analytical tool to detect and quantify 2,4-D levels in environmental samples, and the analytical results can be obtained in about ten minutes. In addition, the nanobody technology used in this study provides an inexhaustible supply of a relatively stable antibodies that can be archived as a nanobody, plasmid or even its sequence.
Keywords: 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid; colorimetric card; gold nanoparticle immunochromatographic strip; nanobody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Tayeb W., Nakbi A., Trabelsi M., Miled A., Hammami M. Biochemical and histological evaluation of kidney damage after sub-acute exposure to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic herbicide in rats: Involvement of oxidative stress. Toxicol. Mech. Methods. 2012;22:696–704. doi: 10.3109/15376516.2012.717650. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ueda R.M.R., Souza V.M.D., Magalhães L.R., Giuffrida R., Nai G.A. Alteration of object recognition memory after chronic exposure to dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in adult rats. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021;10:e23310111695. doi: 10.33448/rsd-v10i1.11695. - DOI
-
- Obidike I.R., Aka L.O., Omoja V.U., Shoyinka S., Kamalu T.N., Anika S.M. Testicular morphology and antispermatogenic effects of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in male West African Dwarf (WAD) goats. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2012;21:1457–1462. doi: 10.1007/s00580-011-1314-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- YJ201963/the starting Scientific Research Founda-tion for the introduced talents of Hebei Agricultural University
- R35 ES030443-01/National Institute of Health RIVER Award
- P42ES004699/the National Institute of Environmental Health Science Superfund Research Program
- R35 ES030443/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 31471786/National Natural Science Foundation of China

