Effect of Short-Term Deep-Pressure Portable Seat on Behavioral and Biological Stress in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 35200402
- PMCID: PMC8869092
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9020048
Effect of Short-Term Deep-Pressure Portable Seat on Behavioral and Biological Stress in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Pilot Study
Abstract
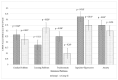
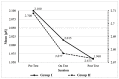
Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) have challenging behaviors, which are associated with difficulties in parenting. Deep pressure is a therapeutic modality in occupational therapy, and it was reported to produce a calming effect. This study aimed to determine whether the short-term use of an autism hug machine portable seat (AHMPS) improves behavioral and neurobiological stress in children with ASD, and to determine whether AHMPS with an inflatable wrap or manual pull is more effective. This study enrolled children with ASD who were administered with the inflatable wrap (group I) and manual pull (group II) for 20 min twice a week for 3 weeks. Conners' Parent Rating Scale-48 (CPRS-48) was used to rate behavioral improvements, and galvanic skin response (GSR) was used to measure sympathetic stress response. A total of 20 children with ASD (14 boys and 6 girls; aged 7-13 years) were included. CPRS-48 presented conduct problems: behavior was significantly decreased in the inflatable group (p = 0.007) compared to the manual pull group. The GSR captured a significant reduction in sympathetic response (p = 0.01) only in group I. Neurobiological stress was reduced in children who were wearing the AHMPS inflatable wrap; therefore, AHMPS inflatable wrap is an effective method to reduce emotional arousal.
Keywords: anxiety; autism spectrum disorders; behavioral problems; deep pressure; hug machine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare there is no conflict of interest regarding this publication. This manuscript has not been published previously and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere. This manuscript has been read and approved by all authors prior to submission.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
-
- Baio J. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2010. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2014;63:1–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

