A Multiscale Partition-Based Kolmogorov-Sinai Entropy for the Complexity Assessment of Heartbeat Dynamics
- PMID: 35200433
- PMCID: PMC8869747
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9020080
A Multiscale Partition-Based Kolmogorov-Sinai Entropy for the Complexity Assessment of Heartbeat Dynamics
Abstract
Background: Several methods have been proposed to estimate complexity in physiological time series observed at different time scales, with a particular focus on heart rate variability (HRV) series. In this frame, while several complexity quantifiers defined in the multiscale domain have already been investigated, the effectiveness of a multiscale Kolmogorov-Sinai (K-S) entropy has not been evaluated yet for the characterization of heartbeat dynamics.
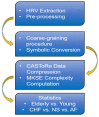
Methods: The use of the algorithmic information content, which is estimated through an effective compression algorithm, is investigated to quantify multiscale partition-based K-S entropy on publicly available experimental HRV series gathered from young and elderly subjects undergoing a visual elicitation task (Fantasia). Moreover, publicly available HRV series gathered from healthy subjects, as well as patients with atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure in unstructured conditions have been analyzed as well.
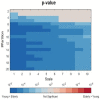
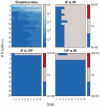
Results: Elderly people are associated with a lower HRV complexity and a more predictable cardiovascular dynamics, with significantly lower partition-based K-S entropy than the young adults. Major differences between these groups occur at partitions greater than six. In case of partition cardinality greater than 5, patients with congestive heart failure show a minimal predictability, while atrial fibrillation shows a higher variability, and hence complexity, which is actually reduced by the time coarse-graining procedure.
Conclusions: The proposed multiscale partition-based K-S entropy is a viable tool to investigate complex cardiovascular dynamics in different physiopathological states.
Keywords: cardiovascular dynamics; complexity; entropy; heart rate variability; signal processing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sauer T., Yorke J.A., Casdagli M. Embedology. J. Stat. Phys. 1991;65:579–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01053745. - DOI
-
- Grassberger P., Procaccia I. Measuring the strangeness of strange attractors. Phys. D. 1983;9:189–208. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(83)90298-1. - DOI
-
- Grassberger P., Procaccia I. Characterization of strange attractors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983;50:346. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.50.346. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

