In Vitro Methods for Measuring the Permeability of Cell Monolayers
- PMID: 35200533
- PMCID: PMC8874757
- DOI: 10.3390/mps5010017
In Vitro Methods for Measuring the Permeability of Cell Monolayers
Abstract
Cell monolayers, including endothelial and epithelial cells, play crucial roles in regulating the transport of biomolecules to underlying tissues and structures via intercellular junctions. Moreover, the monolayers form a semipermeable barrier across which leukocyte transmigration is tightly regulated. The inflammatory cytokines can disrupt the epithelial and endothelial permeability, thus the reduced barrier integrity is a hallmark of epithelial and endothelial dysfunction related with numerous pathological conditions, including cancer-related inflammation. Therefore, the assessment of barrier function is critical in in vitro models of barrier-forming tissues. This review summarizes the commercially available in vitro systems used to measure the permeability of cellular monolayers. The presented techniques are separated in two large groups: macromolecular tracer flux assays, and electrical impedance measurement-based permeability assays. The presented techniques are briefly described and compared.
Keywords: dysfunction; endothelium; epithelium; fluorescent tracer; microfluidics; permeability; transendothelial resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

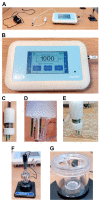
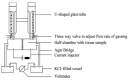
References
-
- Martìn-Padura I., Lostaglio S., Schneemann M., Williams L., Romano M., Fruscella P., Panzeri C., Stoppacciaro A., Ruco L., Villa A., et al. Junctional adhesion molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that distributes at intercellular junctions and modulates monocyte transmigration. J. Cell Biol. 1998;142:117–127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.142.1.117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

