Seaweed Extracts: A Promising Source of Antibiofilm Agents with Distinct Mechanisms of Action against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 35200622
- PMCID: PMC8877608
- DOI: 10.3390/md20020092
Seaweed Extracts: A Promising Source of Antibiofilm Agents with Distinct Mechanisms of Action against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
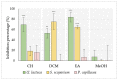
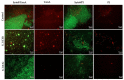
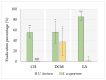
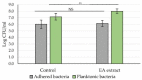
The organization of bacteria in biofilms is one of the adaptive resistance mechanisms providing increased protection against conventional treatments. Thus, the search for new antibiofilm agents for medical purposes, especially of natural origin, is currently the object of much attention. The objective of the study presented here was to explore the potential of extracts derived from three seaweeds: the green Ulva lactuca, the brown Stypocaulon scoparium, and the red Pterocladiella capillacea, in terms of their antibiofilm activity against P. aeruginosa. After preparation of extracts by successive maceration in various solvents, their antibiofilm activity was evaluated on biofilm formation and on mature biofilms. Their inhibition and eradication abilities were determined using two complementary methods: crystal violet staining and quantification of adherent bacteria. The effect of active extracts on biofilm morphology was also investigated by epifluorescence microscopy. Results revealed a promising antibiofilm activity of two extracts (cyclohexane and ethyl acetate) derived from the green alga by exhibiting a distinct mechanism of action, which was supported by microscopic analyses. The ethyl acetate extract was further explored for its interaction with tobramycin and colistin. Interestingly, this extract showed a promising synergistic effect with tobramycin. First analyses of the chemical composition of extracts by GC-MS allowed for the identification of several molecules. Their implication in the interesting antibiofilm activity is discussed. These findings suggest the ability of the green alga U. lactuca to offer a promising source of bioactive candidates that could have both a preventive and a curative effect in the treatment of biofilms.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Ulva lactuca; anti-biofilm; biofilm-matrix; seaweed extracts; synergistic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Seaweed Extracts as an Effective Gateway in the Search for Novel Antibiofilm Agents against Staphylococcus aureus.Plants (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;11(17):2285. doi: 10.3390/plants11172285. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36079667 Free PMC article.
-
An effective antibiofilm agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm from traditional Thai herbal recipes used for wound treatments.Microb Drug Resist. 2013 Oct;19(5):337-43. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2012.0252. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Microb Drug Resist. 2013. PMID: 23600560
-
Biofilm inhibition formation of clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutans, photocatalytic activity of azo dye and GC-MS analysis of leaves of Lagerstroemia speciosa.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017 Apr;169:148-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.03.007. Epub 2017 Mar 9. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017. PMID: 28319869
-
Evolving biofilm inhibition and eradication in clinical settings through plant-based antibiofilm agents.Phytomedicine. 2023 Oct;119:154973. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154973. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37499434 Review.
-
Marine microbial enzymes as potential antibiofilm agents: expanding the arsenal of bioactive agents targeting biofilm-forming microorganisms.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2025 May 29:1-18. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2025.2510247. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40439000 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Potential of Algal Extracts as Promising Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Agents against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: In Vitro and In Silico Studies including Molecular Docking.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 20;12(18):3324. doi: 10.3390/plants12183324. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765485 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Biofilm Extracts and Molecules from the Marine Environment.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jul 10;22(7):313. doi: 10.3390/md22070313. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39057422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active Targeting of P-Selectin by Fucoidan Modulates the Molecular Profiling of Metastasis in Docetaxel-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Mar Drugs. 2022 Aug 23;20(9):542. doi: 10.3390/md20090542. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36135731 Free PMC article.
-
Antifouling activity of Malaysian green seaweed Ulva lactuca and its isolated non-polar compound.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 24;10(19):e38366. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38366. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39397965 Free PMC article.
-
Seaweed Extracts as an Effective Gateway in the Search for Novel Antibiofilm Agents against Staphylococcus aureus.Plants (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;11(17):2285. doi: 10.3390/plants11172285. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36079667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Develipment of New Antibiotics. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

