Chitosan-Based Films with 2-Aminothiophene Derivative: Formulation, Characterization and Potential Antifungal Activity
- PMID: 35200633
- PMCID: PMC8878255
- DOI: 10.3390/md20020103
Chitosan-Based Films with 2-Aminothiophene Derivative: Formulation, Characterization and Potential Antifungal Activity
Abstract
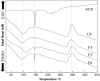
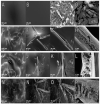
In this study, films of chitosan and 2-amino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carbonitrile (6CN), a 2-aminothiophene derivative with great pharmacological potential, were prepared as a system for a topical formulation. 6CN-chitosan films were characterized by physicochemical analyses, such as Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electronic microscopy (SEM). Additionally, the antifungal potential of the films was evaluated in vitro against three species of Candida (C. albicans, C. tropicalis, and C. parapsilosis). The results of the FTIR and thermal analysis showed the incorporation of 6CN in the polymer matrix. In the diffractogram, the 6CN-chitosan films exhibited diffraction halos that were characteristic of amorphous structures, while the micrographs showed that 6CN particles were dispersed in the chitosan matrix, exhibiting pores and cracks on the film surface. In addition, the results of antifungal investigation demonstrated that 6CN-chitosan films were effective against Candida species showing potential for application as a new antifungal drug.
Keywords: 2-aminothiophene derivative; antifungal activity; chitosan; films.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Kummari L.K., Butler M.S., Furlong E., Blundell R., Nouwens A., Silva A.B., Kappler U., Fraser J.A., Kobe B., Cooper M.A., et al. Antifungal benzo[b]thiophene 1,1-dioxide IMPDH inhibitors exhibit pan- assay interference (PAINS) profiles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018;26:5408–5419. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.09.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scotti L., Scotti M.T., De Oliveira Lima E., Da Silva M.S., Do Carmo Alves De Lima M., Da Rocha Pitta I., De Moura R.O., De Oliveira J.G.B., Da Cruz R.M.D., Mendonça F.J.B. Experimental methodologies and evaluations of computer-aided drug design methodologies applied to a series of 2-aminothiophene derivatives with antifungal activities. Molecules. 2012;17:2298–2315. doi: 10.3390/molecules17032298. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mendonça F.J.B., Lima-Neto R.G., de Oliveira T.B., de Lima M.C.A., Pitta I.R., Galdino S.L., da Cruz R.M.D., de Araújo R.S.A., Neves R.P. Synthesis and evaluation of the antifungal activity of 2-(substituted-amino)-4,5-dialkyl-thiophene-3-carbonitrile derivatives. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2011;30:1492–1499.
-
- de Araújo Neto L.N., do Carmo Alves de Lima M., de Oliveira J.F., de Souza E.R., Buonafina M.D.S., Vitor Anjos M.N., Brayner F.A., Alves L.C., Neves R.P., Mendonça-Junior F.J.B. Synthesis, cytotoxicity and antifungal activity of 5-nitro-thiophene-thiosemicarbazones derivatives. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017;272:172–181. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.05.005. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

