An Overview of Potential Seaweed-Derived Bioactive Compounds for Pharmaceutical Applications
- PMID: 35200670
- PMCID: PMC8875101
- DOI: 10.3390/md20020141
An Overview of Potential Seaweed-Derived Bioactive Compounds for Pharmaceutical Applications
Abstract
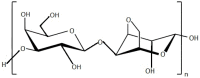
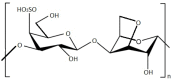
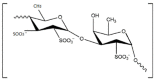
Nowadays, seaweeds are widely involved in biotechnological applications. Due to the variety of bioactive compounds in their composition, species of phylum Ochrophyta, class Phaeophyceae, phylum Rhodophyta and Chlorophyta are valuable for the food, cosmetic, pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. Seaweeds have been consumed as whole food since ancient times and used to treat several diseases, even though the mechanisms of action were unknown. During the last decades, research has demonstrated that those unique compounds express beneficial properties for human health. Each compound has peculiar properties (e.g., antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiviral activities, etc.) that can be exploited to enhance human health. Seaweed's extracted polysaccharides are already involved in the pharmaceutical industry, with the aim of replacing synthetic compounds with components of natural origin. This review aims at a better understanding of the recent uses of algae in drug development, with the scope of replacing synthetic compounds and the multiple biotechnological applications that make up seaweed's potential in industrial companies. Further research is needed to better understand the mechanisms of action of seaweed's compounds and to embrace the use of seaweeds in pharmaceutical companies and other applications, with the final scope being to produce sustainable and healthier products.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; health benefits; pharmaceutical application; seaweed; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
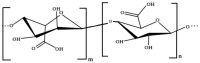
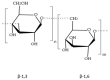
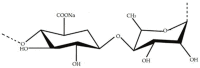
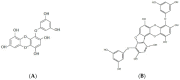
References
-
- Pereira L. Biological and therapeutic properties of the seaweed polysaccharides. Int. Biol. Rev. 2018;2:1–50. doi: 10.18103/ibr.v2i2.1762. - DOI
-
- Bixler H.J., Porse H. A decade of change in the seaweed hydrocolloids industry. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011;23:321–335. doi: 10.1007/s10811-010-9529-3. - DOI
-
- Khotimchenko S.V., Vaskovsky V.E., Titlyanova T.V. Fatty acids of marine algae from the pacific coast of North California. Bot. Mar. 2002;45:17–22. doi: 10.1515/BOT.2002.003. - DOI
-
- Agregán R., Munekata P.E., Domínguez R., Carballo J., Franco D., Lorenzo J.M. Proximate composition, phenolic content and in vitro antioxidant activity of aqueous extracts of the seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum, Bifurcaria bifurcata and Fucus vesiculosus. Effect of addition of the extracts on the oxidative stability of canola oil unde. Food Res. Int. 2017;99:986–994. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.11.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

