Assessment of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss After COVID-19 Vaccination
- PMID: 35201274
- PMCID: PMC8874871
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoto.2021.4414
Assessment of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss After COVID-19 Vaccination
Erratum in
-
Error in Data.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Nov 1;148(11):1082. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2022.3635. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36355364 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Emerging reports of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) after COVID-19 vaccination within the otolaryngological community and the public have raised concern about a possible association between COVID-19 vaccination and the development of SSNHL.
Objective: To examine the potential association between COVID-19 vaccination and SSNHL.
Design, setting, and participants: This cross-sectional study and case series involved an up-to-date population-based analysis of 555 incident reports of probable SSNHL in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) over the first 7 months of the US vaccination campaign (December 14, 2020, through July 16, 2021). In addition, data from a multi-institutional retrospective case series of 21 patients who developed SSNHL after COVID-19 vaccination were analyzed. The study included all adults experiencing SSNHL within 3 weeks of COVID-19 vaccination who submitted reports to VAERS and consecutive adult patients presenting to 2 tertiary care centers and 1 community practice in the US who were diagnosed with SSNHL within 3 weeks of COVID-19 vaccination.
Exposures: Receipt of a COVID-19 vaccine produced by any of the 3 vaccine manufacturers (Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, or Janssen/Johnson & Johnson) used in the US.
Main outcomes and measures: Incidence of reports of SSNHL after COVID-19 vaccination recorded in VAERS and clinical characteristics of adult patients presenting with SSNHL after COVID-19 vaccination.
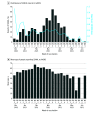
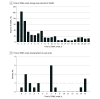
Results: A total of 555 incident reports in VAERS (mean patient age, 54 years [range, 15-93 years]; 305 women [55.0%]; data on race and ethnicity not available in VAERS) met the definition of probable SSNHL (mean time to onset, 6 days [range, 0-21 days]) over the period investigated, representing an annualized incidence estimate of 0.6 to 28.0 cases of SSNHL per 100 000 people per year. The rate of incident reports of SSNHL was similar across all 3 vaccine manufacturers (0.16 cases per 100 000 doses for both Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines, and 0.22 cases per 100 000 doses for Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine). The case series included 21 patients (mean age, 61 years [range, 23-92 years]; 13 women [61.9%]) with SSNHL, with a mean time to onset of 6 days (range, 0-15 days). Patients were heterogeneous with respect to clinical and demographic characteristics. Preexisting autoimmune disease was present in 6 patients (28.6%). Of the 14 patients with posttreatment audiometric data, 8 (57.1%) experienced improvement after receiving treatment. One patient experienced SSNHL 14 days after receiving each dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.
Conclusions and relevance: In this cross-sectional study, findings from an updated analysis of VAERS data and a case series of patients who experienced SSNHL after COVID-19 vaccination did not suggest an association between COVID-19 vaccination and an increased incidence of hearing loss compared with the expected incidence in the general population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Rare Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Potentially Associated With COVID-19 Vaccination Does Not Outweigh the Benefit of COVID-19 Vaccines.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Apr 1;148(4):315-316. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2021.4279. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 35201285 No abstract available.
-
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and COVID-19 Vaccination Revisited-An Ongoing Conversation-Reply.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Aug 1;148(8):795-796. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2022.1603. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 35771537 No abstract available.
References
-
- Asatryan A, Pool V, Chen RT, Kohl KS, Davis RL, Iskander JK; VAERS Team . Live attenuated measles and mumps viral strain–containing vaccines and hearing loss: Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), United States, 1990-2003. Vaccine. 2008;26(9):1166-1172. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.12.049 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Formeister EJ, Chien W, Agrawal Y, Carey JP, Stewart CM, Sun DQ. Preliminary analysis of association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden hearing loss using US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System data. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;147(7):674-676. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2021.0869 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . COVID data tracker. 2021. Accessed July 23, 2021. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#datatracker-home
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

