Risk of Opioid Overdose Associated With Concomitant Use of Oxycodone and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
- PMID: 35201310
- PMCID: PMC8874341
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.0194
Risk of Opioid Overdose Associated With Concomitant Use of Oxycodone and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
Abstract
Importance: Some selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) inhibit the enzymes responsible for the metabolism of oxycodone, a potent prescription opioid. The clinical consequences of this interaction on the risk of opioid overdose have not been elucidated.
Objective: To compare opioid overdose rates in patients initiating oxycodone while taking SSRIs that are potent inhibitors of the cytochrome-P450 2D6 enzyme (CYP2D6) vs SSRIs that are not.
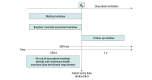
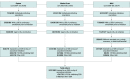
Design, setting, and participants: This cohort study included adults who initiated oxycodone while receiving SSRI therapy between 2000 and 2020 whose data were included in 3 US health insurance databases.
Exposures: Use of SSRIs that strongly inhibit CYP2D6 enzyme (fluoxetine or paroxetine) vs use of other SSRIs at the time of oxycodone initiation.
Main outcomes and measures: Opioid overdose hospitalization or emergency department visit. Outcomes were assessed within 365 days of oxycodone initiation; in primary analyses, patients were followed up until the discontinuation of either oxycodone or their index SSRI group. Propensity score matching weights were used to adjust for confounding. Crude and weighted (adjusted) incidence rates and hazard ratios were estimated using Cox regression models, separately within each database and overall, stratifying on database.
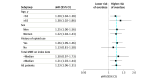
Results: A total of 2 037 490 initiated oxycodone while taking SSRIs (1 475 114 [72.4%] women; mean [SD] age, 50.1 [15.3] years). Most (1 418 712 [69.6%]) were receiving other SSRIs at the time of oxycodone initiation. In the primary analysis, we observed 1035 overdose events (0.05% of the study cohort). The adjusted incidence rate of opioid overdose in those using inhibiting SSRIs at the time of oxycodone initiation (9.47 per 1000 person-years) was higher than in those using other SSRIs (7.66 per 1000 person-years), indicating a greater risk of overdose among patients using CYP2D6-inhibiting SSRIs (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.06-1.31). Results were consistent across multiple subgroup and sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions and relevance: In this cohort study of US adults, initiating oxycodone in patients treated with paroxetine or fluoxetine was associated with a small increased risk of opioid overdose.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk of mortality with concomitant use of tamoxifen and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: multi-database cohort study.BMJ. 2016 Sep 30;354:i5014. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i5014. BMJ. 2016. PMID: 27694571 Free PMC article.
-
[Serotoninergic antidepressants and opiate analgesics: a sometimes-painful association. A case report].Encephale. 2010 Jun;36 Suppl 2:D119-23. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2009.03.010. Epub 2009 Aug 29. Encephale. 2010. PMID: 20513454 French.
-
Economic consequences of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use with drugs also metabolized by the cytochrome P-450 system.Clin Ther. 1998 Jul-Aug;20(4):780-96. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(98)80141-0. Clin Ther. 1998. PMID: 9737837
-
Systematic review and guide to selection of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.Drugs. 1999 Apr;57(4):507-33. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199957040-00005. Drugs. 1999. PMID: 10235690
-
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationship of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1996 Dec;31(6):444-69. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199631060-00004. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1996. PMID: 8968657 Review.
Cited by
-
Co-prescribing of Central Nervous System-Active Medications for COPD Patients: Impact on Emergency Room Visits and Hospitalization.Ann Pharmacother. 2023 Apr;57(4):382-396. doi: 10.1177/10600280221113299. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Ann Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 35942598 Free PMC article.
-
Psychiatric Comorbidity Does Not Enhance Prescription Opioid Use in Inflammatory Bowel Disease as It Does in the General Population.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2025 Feb 10;31(2):386-393. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izae188. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2025. PMID: 39226051 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Drug-Drug Interactions in Pharmacoepidemiologic Research.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2025 Jan;34(1):e70088. doi: 10.1002/pds.70088. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2025. PMID: 39805810 Review.
-
Clinical and Adverse Outcomes Associated With Concomitant Use of CYP2D6-Metabolized Opioids With Antidepressants in Older Nursing Home Residents : A Target Trial Emulation Study.Ann Intern Med. 2024 Aug;177(8):1058-1068. doi: 10.7326/M23-3109. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Ann Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 39038293 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Overactive Bladder Drugs and the Risk of Urinary Tract Infection.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2024 May;115(5):1132-1140. doi: 10.1002/cpt.3182. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38284421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) . Wide-ranging online data for epidemiologic research (WONDER). Accessed July 15, 2021. http://wonder.cdc.gov

