Urinary tetrahydroaldosterone is associated with circulating FGF23 in kidney stone formers
- PMID: 35201364
- PMCID: PMC9110437
- DOI: 10.1007/s00240-022-01317-2
Urinary tetrahydroaldosterone is associated with circulating FGF23 in kidney stone formers
Abstract
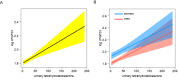
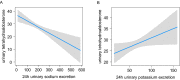
The spectrum of diseases with overactive renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAS) or elevated circulating FGF23 overlaps, but the relationship between aldosterone and FGF23 remains unclarified. Here, we report that systemic RAS activation sensitively assessed by urinary tetrahydroaldosterone excretion is associated with circulating C-terminal FGF23. We performed a retrospective analysis in the Bern Kidney Stone Registry, a single-center observational cohort of kidney stone formers. Urinary excretion of the main aldosterone metabolite tetrahydroaldosterone was measured by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Plasma FGF23 concentrations were measured using a C-terminal assay. Regression models were calculated to assess the association of plasma FGF23 with 24 h urinary tetrahydroaldosterone excretion. We included 625 participants in the analysis. Mean age was 47 ± 14 years and 71% were male. Mean estimated GFR was 94 ml/min per 1.73 m2. In unadjusted analyses, we found a positive association between plasma FGF23 and 24 h urinary tetrahydroaldosterone excretion (β: 0.0027; p = 4.2 × 10-7). In multivariable regression models adjusting for age, sex, body mass index and GFR, this association remained robust (β: 0.0022; p = 2.1 × 10-5). Mineralotropic hormones, 24 h urinary sodium and potassium excretion as surrogates for sodium and potassium intake or antihypertensive drugs did not affect this association. Our data reveal a robust association of RAS activity with circulating FGF23 levels in kidney stone formers. These findings are in line with previous studies in rodents and suggest a physiological link between RAS system activation and FGF23 secretion.
Keywords: Aldosterone; FGF23; Renin–angiotensin system; Steroid metabolite; Tetrahydroaldosterone.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DGF has served as a consultant for Otsuka Pharmaceuticals and Alnylam, and has received unrestricted research funding from Novartis, Abbvie, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals and Boehringer Ingelheim.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urinary Potassium Excretion, Fibroblast Growth Factor 23, and Incident Hypertension in the General Population-Based PREVEND Cohort.Nutrients. 2021 Dec 17;13(12):4532. doi: 10.3390/nu13124532. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34960084 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary tetrahydroaldosterone as a screening method for primary aldosteronism: a comparative study.Am J Hypertens. 2003 Jul;16(7):522-30. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(03)00858-6. Am J Hypertens. 2003. PMID: 12850384
-
Urinary sodium excretion is the main determinant of mineralocorticoid excretion rates in patients with chronic kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Jun;28(6):1526-32. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft007. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23413088
-
Improved gas chromatographic-mass fragmentographic assay for tetrahydroaldosterone and aldosterone in urine.J Chromatogr. 1986 Jun 13;378(2):283-92. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80725-2. J Chromatogr. 1986. PMID: 3733988
-
Dietary treatment of urinary risk factors for renal stone formation. A review of CLU Working Group.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2015 Jul 7;87(2):105-20. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2015.2.105. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2015. PMID: 26150027 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Effects of Laparoscopic Surgery and Traditional Open Surgery on Stone Clearance, Laboratory Indexes and Life Quality in Patients with Renal Calculi.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Sep 29;2022:8211389. doi: 10.1155/2022/8211389. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9817359. doi: 10.1155/2023/9817359. PMID: 36213585 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Imazu M, Takahama H, Asanuma H, Funada A, Sugano Y, Ohara T, Hasegawa T, Asakura M, Kanzaki H, Anzai T, Kitakaze M. Pathophysiological impact of serum fibroblast growth factor 23 in patients with nonischemic cardiac disease and early chronic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;307:H1504–1511. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00331.2014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akhabue E, Vu T-HT, Vaidya A, Michos ED, de Boer IH, Kestenbaum B, Allison M, Szklo M, Ouyang P, Yancy CW, Wolf M, Isakova T, Carnethon MR. Fibroblast growth factor-23, heart failure risk, and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system blockade in hypertension: the MESA study. Am J Hypertens. 2019;32:18–25. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpy142. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ter Maaten JM, Voors AA, Damman K, van der Meer P, Anker SD, Cleland JG, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, van der Harst P, Hillege HL, Lang CC, Metra M, Navis G, Ng L, Ouwerkerk W, Ponikowski P, Samani NJ, van Veldhuisen DJ, Zannad F, Zwinderman AH, de Borst MH. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is related to profiles indicating volume overload, poor therapy optimization and prognosis in patients with new-onset and worsening heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 2018;253:84–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.10.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Humalda JK, Riphagen IJ, Assa S, Hummel YM, Westerhuis R, Vervloet MG, Voors AA, Navis G, Franssen CFM, de Borst MH, NIGRAM Consortium Fibroblast growth factor 23 correlates with volume status in haemodialysis patients and is not reduced by haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant Off Publ Eur Dial Transpl Assoc-Eur Ren Assoc. 2016;31:1494–1501. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv393. - DOI - PubMed

