Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma versus conventional hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35201426
- PMCID: PMC11801166
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-03949-8
Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma versus conventional hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma (SHCC) is a rare subtype of primary liver malignancies and is still ill-defined and poorly understood. Therefore, our study was performed to have a comprehensive evaluation SHCC versus conventional hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
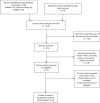
Methods: A thorough database searching was performed in PubMed, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library. RevMan5.3 and Stata 13.0 software were used for statistical analyses. The primary endpoint of our analysis is the long-term survival and the secondary endpoint is clinical and pathological features.
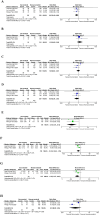
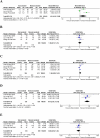
Results: Four studies with a relative large cohort were finally identified. Compared with patients with pure HCC, patients with SHCC had a significantly worse overall survival (P < 0.00001) and disease-free survival (P < 0.0001). Moreover, a larger tumor size (P = 0.003), a higher incidence of node metastasis (P < 0.00001) and a higher proportion of advanced lesions (P = 0.04) were more frequently detected in patients with SHCC. Higher levels of serum ALT (P = 0.02) and TB (P = 0.005) were detected in patients with HCC rather than SHCC, while serum ALB (P = 0.02) level was relatively higher in patients with SHCC. For other measured outcomes, including concurrent viral hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, liver storage (Child A/B), multifocal tumors, vascular invasion and preoperative AFP level, the results showed no significant difference (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: SHCC has a worse prognosis and exhibits more aggressively than conventional HCC. Future large well-designed studies are demanded for further validation.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Prognosis; Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- ZYJC21046/1.3.5 project for disciplines of excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University
- 2021HXFH001/1.3.5 project for disciplines of excellence-Clinical Research Incubation Project, West China Hospital, Sichuan University
- 2021YFS0100/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- 2021M692277/The fellowship of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2021CDZG-23/Sichuan University-Zigong School-local Cooperation project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

