Genome sequences of Arthrobacter spp. that use a modified sulfoglycolytic Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway
- PMID: 35201431
- PMCID: PMC8873060
- DOI: 10.1007/s00203-022-02803-2
Genome sequences of Arthrobacter spp. that use a modified sulfoglycolytic Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway
Abstract
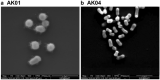
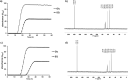
Sulfoglycolysis pathways enable the breakdown of the sulfosugar sulfoquinovose and environmental recycling of its carbon and sulfur content. The prototypical sulfoglycolytic pathway is a variant of the classical Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) pathway that results in formation of 2,3-dihydroxypropanesulfonate and was first described in gram-negative Escherichia coli. We used enrichment cultures to discover new sulfoglycolytic bacteria from Australian soil samples. Two gram-positive Arthrobacter spp. were isolated that produced sulfolactate as the metabolic end-product. Genome sequences identified a modified sulfoglycolytic EMP gene cluster, conserved across a range of other Actinobacteria, that retained the core sulfoglycolysis genes encoding metabolic enzymes but featured the replacement of the gene encoding sulfolactaldehyde (SLA) reductase with SLA dehydrogenase, and the absence of sulfoquinovosidase and sulfoquinovose mutarotase genes. Excretion of sulfolactate by these Arthrobacter spp. is consistent with an aerobic saprophytic lifestyle. This work broadens our knowledge of the sulfo-EMP pathway to include soil bacteria.
Keywords: Enrichment; Isotope labeling; Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy; Sulfur cycle.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Benson AA, Shibuya I. Sulfocarbohydrate metabolism. Fed Proc. 1961;20:79.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

