microRNA-26a represses pancreatic cancer cell malignant behaviors by targeting E2F7
- PMID: 35201478
- PMCID: PMC8777553
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-021-00448-z
microRNA-26a represses pancreatic cancer cell malignant behaviors by targeting E2F7
Abstract
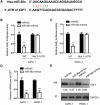
Dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) exerts key roles in the development of pancreatic cancer (PCa). miR-26a is reportedly a tumor suppressor in cancers. However, whether miR-26a modulates PCa progression is poorly understood. Here, we found that miR-26a was down-regulated in PCa. Overexpressed miR-26a suppressed PCa cell proliferation, colony formation, and tumor stem cell properties. Mechanically, the transcription factor E2F7 is a downstream target of miR-26a. miR-26a decreased E2F7 expression through binding to the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of E2F7. Decreased miR-26a in PCa tissues was inversely correlated with E2F7. The inhibitory effects of miR-26a in PCa were reversed by E2F7 overexpression. Consistently, the knockout of E2F7 further significantly inhibited the growth of PCa cells combined with miR-26a overexpression. Further study revealed that E2F7 bound the promoter of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), a key factor in angiogenesis, and transcriptionally activated the expression of VEGFA. miR-26a overexpression attenuated the effects of E2F7 on VEGFA promotion. Our results uncovered the novel function of miR-26a/E2F7/VEGFA in PCa, making miR-26a a possible target for PCa treatment.
Keywords: Cell proliferation; E2F7; Pancreatic cancer; VEGFA; miR-26a.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
