Promoter-Bound Full-Length Intronic Circular RNAs-RNA Polymerase II Complexes Regulate Gene Expression in the Human Parasite Entamoeba histolytica
- PMID: 35202086
- PMCID: PMC8876499
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna8010012
Promoter-Bound Full-Length Intronic Circular RNAs-RNA Polymerase II Complexes Regulate Gene Expression in the Human Parasite Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
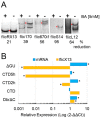
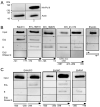
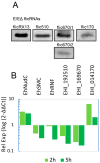
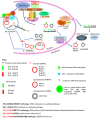
Ubiquitous eukaryotic non-coding circular RNAs are involved in numerous co- and post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Recently, we reported full-length intronic circular RNAs (flicRNAs) in Entamoeba histolytica, with 3'ss-5'ss ligation points and 5'ss GU-rich elements essential for their biogenesis and their suggested role in transcription regulation. Here, we explored how flicRNAs impact gene expression regulation. Using CLIP assays, followed by qRT-PCR, we identified that the RabX13 control flicRNA and virulence-associated flicRNAs were bound to the HA-tagged RNA Pol II C-terminus domain in E. histolytica transformants. The U2 snRNA was also present in such complexes, indicating that they belonged to transcription initiation/elongation complexes. Correspondingly, inhibition of the second step of splicing using boric acid reduced flicRNA formation and modified the expression of their parental genes and non-related genes. flicRNAs were also recovered from chromatin immunoprecipitation eluates, indicating that the flicRNA-Pol II complex was formed in the promoter of their cognate genes. Finally, two flicRNAs were found to be cytosolic, whose functions remain to be uncovered. Here, we provide novel evidence of the role of flicRNAs in gene expression regulation in cis, apparently in a widespread fashion, as an element bound to the RNA polymerase II transcription initiation complex, in E. histolytica.
Keywords: Pol II-CTD; circRNA; flicRNA; gene promoter; splicing; transcription regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

