Interdependent Transcription of a Natural Sense/Antisense Transcripts Pair (SLC34A1/PFN3)
- PMID: 35202092
- PMCID: PMC8877773
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna8010019
Interdependent Transcription of a Natural Sense/Antisense Transcripts Pair (SLC34A1/PFN3)
Abstract
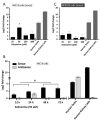
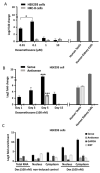
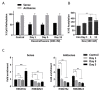
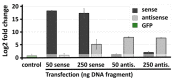
Natural antisense transcripts (NATs) constitute a significant group of regulatory, long noncoding RNAs. They are prominently expressed in testis but are also detectable in other organs. NATs are transcribed at low levels and co-expressed with related protein coding sense transcripts. Nowadays NATs are generally considered as regulatory, long noncoding RNAs without closer focus on the inevitable interference between sense and antisense expression. This work describes a cellular system where sense and antisense transcription of a specific locus (SLC34A1/PFN3) is induced using epigenetic modifiers and CRISPR-Cas9. The renal cell lines HEK293 and HKC-8 do not express SLC34A1/PFN3 under normal culture conditions. Five-day exposure to dexamethasone significantly stimulates sense transcript (SLC34A1) levels and antisense (PFN3) minimally; the effect is only seen in HEK293 cells. Enhanced expression is paralleled by reduced sense promoter methylation and an increase in activating histone marks. Expression is further modulated by cassettes that stimulate the expression of sense or antisense transcript but disrupt protein coding potential. Constitutive expression of a 5'-truncated SLC34A1 transcript increases sense expression independent of dexamethasone induction but also stimulates antisense expression. Concordant expression is confirmed with the antisense knock-in that also enhances sense expression. The antisense effect acts on transcription in cis since transient transfection with sense or antisense constructs fails to stimulate the expression of the opposite transcript. These results suggest that bi-directional transcription of the SLC34A1/PFN3 locus has a stimulatory influence on the expression of the opposite transcript involving epigenetic changes of the promoters. In perspective of extensive, previous research into bi-directionally transcribed SLC34A loci, the findings underpin a hypothesis where NATs display different biological roles in soma and germ cells. Accordingly, we propose that in somatic cells, NATs act like lncRNAs-with the benefit of close proximity to a potential target gene. In germ cells, however, recent evidence suggests different biological roles for NATs that require RNA complementarity and double-stranded RNA formation.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; DNA methylation; concordant expression; histone modifications; natural antisense transcripts; transcriptional interference.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Natural antisense transcripts as versatile regulators of gene expression.Nat Rev Genet. 2024 Oct;25(10):730-744. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00723-z. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Nat Rev Genet. 2024. PMID: 38632496 Review.
-
Natural antisense transcription from a comparative perspective.Genomics. 2016 Aug;108(2):56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 May 27. Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27241791 Free PMC article.
-
Strand selective generation of endo-siRNAs from the Na/phosphate transporter gene Slc34a1 in murine tissues.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(7):2274-82. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp088. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19237395 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Antisense Transcripts at the Interface between Host Genome and Mobile Genetic Elements.Front Microbiol. 2017 Nov 20;8:2292. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02292. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29209299 Free PMC article.
-
Natural antisense transcripts regulate gene expression in an epigenetic manner.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 May 28;396(2):177-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.147. Epub 2010 May 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20438699 Review.
Cited by
-
The seeds of its regulation: Natural antisense transcripts as single-gene control switches in neurodegenerative disorders.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Aug;99:102336. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102336. Epub 2024 May 11. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38740308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics and transcriptomics profiling reveals distinct aspects of kidney stone related genes in calculi rats.BMC Genomics. 2023 Mar 17;24(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09222-7. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36932340 Free PMC article.
-
Natural antisense transcripts as versatile regulators of gene expression.Nat Rev Genet. 2024 Oct;25(10):730-744. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00723-z. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Nat Rev Genet. 2024. PMID: 38632496 Review.
-
Correlation between the RNA Expression and the DNA Methylation of Estrogen Receptor Genes in Normal and Malignant Human Tissues.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 19;46(4):3610-3625. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040226. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666956 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

