Ultra-Long-Term Therapy of Benign Essential Blepharospasm with Botulinumtoxin A-30 Years of Experience in a Tertiary Care Center
- PMID: 35202148
- PMCID: PMC8875585
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14020120
Ultra-Long-Term Therapy of Benign Essential Blepharospasm with Botulinumtoxin A-30 Years of Experience in a Tertiary Care Center
Abstract
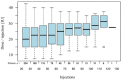
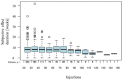
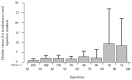
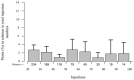
Aim of this study was to investigate the long-term results of botulinum toxin A (BoNT-A) injections for the treatment of benign essential blepharospasm (BEB) and to report our experience with (ultra-)long-term treatment with onabotulinumtoxin-A. We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional analysis at a university hospital. Patients with BEB and BoNT-A treatment were assigned to the Total Blepharospasm Group, patients with ≥21 onabotulinumtoxin-A injections to the Ona Long-Term Group. The Total Blepharospasm Group (n = 1940) included 33,933 BoNT-A injections. The age of patients at symptom onset was (mean ± SD) 58.0 ± 13.1 years, and 70.4% were female. The Ona long-term group (n = 234) included 10,632 onabotulinumtoxin-A injections. In this group, patients received 45.4 ± 22.9 injections with a mean dose of 22.2 IU ± 0.5. The duration of treatment was 12.6 ± 5.4 years, ranging from 2.9 to 30.0 years. The effect-duration-dose quotient did not change during long-term treatment. The observed side effects were comparable in type and frequency to other studies, even with the (ultra-)long treatment with onabotulinumtoxin-A. Our results, based on one of the largest patient populations and a treatment duration of up to 30 years, impressively demonstrate that onabotulinumtoxin-A is a safe and effective therapy for essential blepharospasm, even in the ultra-long term.
Keywords: adverse events; blepharospasm; botulinum toxin; long-term; outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
B.W. has received honoraria and travel grants from Merz and Desitin and research grants from Allergan and Merz. R.F. has no financial interests. P.R. received honoraria from Desitin. The sponsor had no influence on the choice of the research subject nor the design of the study, the representation or interpretation of the findings.
Figures

References
-
- Roggenkämper P., Laskawi R. Botulinumtoxin-Therapie im Kopf-Hals-Bereich. Urban&Vogel; München, Germany: 2004.
-
- ESDE Epidemiological study of dystonia in Europe. J. Neurol. 2000;247:787–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

