Transgenerational Effects of Prenatal Endocrine Disruption on Reproductive and Sociosexual Behaviors in Sprague Dawley Male and Female Rats
- PMID: 35202233
- PMCID: PMC8875130
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10020047
Transgenerational Effects of Prenatal Endocrine Disruption on Reproductive and Sociosexual Behaviors in Sprague Dawley Male and Female Rats
Abstract
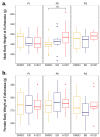
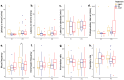
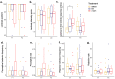
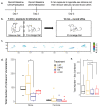
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) lead to endocrine and neurobehavioral changes, particularly due to developmental exposures during gestation and early life. Moreover, intergenerational and transgenerational phenotypic changes may be induced by germline exposure (F2) and epigenetic germline transmission (F3) generation, respectively. Here, we assessed reproductive and sociosexual behavioral outcomes of prenatal Aroclor 1221 (A1221), a lightly chlorinated mix of PCBs known to have weakly estrogenic mechanisms of action; estradiol benzoate (EB), a positive control; or vehicle (3% DMSO in sesame oil) in F1-, F2-, and F3-generation male and female rats. Treatment with EDCs was given on embryonic day (E) 16 and 18, and F1 offspring monitored for development and adult behavior. F2 offspring were generated by breeding with untreated rats, phenotyping of F2s was performed in adulthood, and the F3 generation were similarly produced and phenotyped. Although no effects of treatment were found on F1 or F3 development and physiology, in the F2 generation, body weight in males and uterine weight in females were increased by A1221. Mating behavior results in F1 and F2 generations showed that F1 A1221 females had a longer latency to lordosis. In males, the F2 generation showed decreased mount frequency in the EB group. In the F3 generation, numbers of ultrasonic vocalizations were decreased by EB in males, and by EB and A1221 when the sexes were combined. Finally, partner preference tests in the F3 generation revealed that naïve females preferred F3-EB over untreated males, and that naïve males preferred untreated over F3-EB or F3-A1221 males. As a whole, these results show that each generation has a unique, sex-specific behavioral phenotype due to direct or ancestral EDC exposure.
Keywords: Aroclor 1221 (A1221); endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC); estradiol; mating behavior; paced mating; polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB); social behavior; transgenerational; ultrasonic vocalization (USV).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Zoeller R.T., Brown T.R., Doan L.L., Gore A.C., Skakkebaek N.E., Soto A.M., Woodruff T.J., Vom Saal F.S. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Public Health Protection: A Statement of Principles from The Endocrine Society. Endocrinology. 2012;153:4097–4110. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1422. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

