Environmental Risk Assessment of Oxaliplatin Exposure on Early Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- PMID: 35202267
- PMCID: PMC8880521
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10020081
Environmental Risk Assessment of Oxaliplatin Exposure on Early Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Erratum in
-
Correction: Di Paola et al. Environmental Risk Assessment of Oxaliplatin Exposure on Early Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 81.Toxics. 2024 Dec 31;13(1):28. doi: 10.3390/toxics13010028. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39841031 Free PMC article.
Abstract
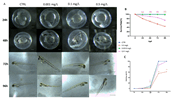
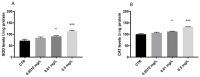
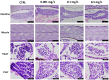
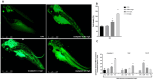
Pharmaceuticals are actually identified as a threat to the ecosystem. Nowadays, the growing consumption of antineoplastic agents has been related to their continuous input in natural environments. These substances can interfere with physiological and biochemical processes of aquatic species over their entire life cycle. Oxaliplatin (OXA) is a widely used chemotherapeutic agent to treat colon or rectal cancer. This study was aimed to evaluate the developmental toxicity of the OXA exposure. To this end, zebrafish embryos were incubated with 0.001, 0.1, 0.5 mg/L OXA. At different timepoints mortality rate, hatching rate, developmental abnormalities, histological analysis, oxidative stress and mRNA expression of gene related to oxidative stress were evaluated. Our results showed that OXA exposure can induce increased mortality and developmental abnormalities reducing the hatching rate. Histological analysis demonstrated that OXA induced liver, intestine, muscle and heart injury. Superoxide dismutase and catalase activities were significantly increased after OXA exposure demonstrating its oxidative effects. The mRNA expression levels of apoptosis-related genes (caspase-3, bax and bcl-2) were significantly upregulated by OXA exposure. In conclusion, we highlighted that OXA exposure led to a dose-related developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Keywords: ROS; cell death; developmental toxicity; oxaliplatin.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Poklar N.a., Pilch D.S., Lippard S.J., Redding E.A., Dunham S.U., Breslauer K.J. Influence of cisplatin intrastrand crosslinking on the conformation, thermal stability, and energetics of a 20-mer DNA duplex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1996;93:7606–7611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7606. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raymond E., Faivre S., Woynarowski J.M., Chaney S.G. Oxaliplatin: Mechanism of action and antineoplastic activity. Semin. Oncol. 1998;25:4–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

